 পেছনে
পেছনে
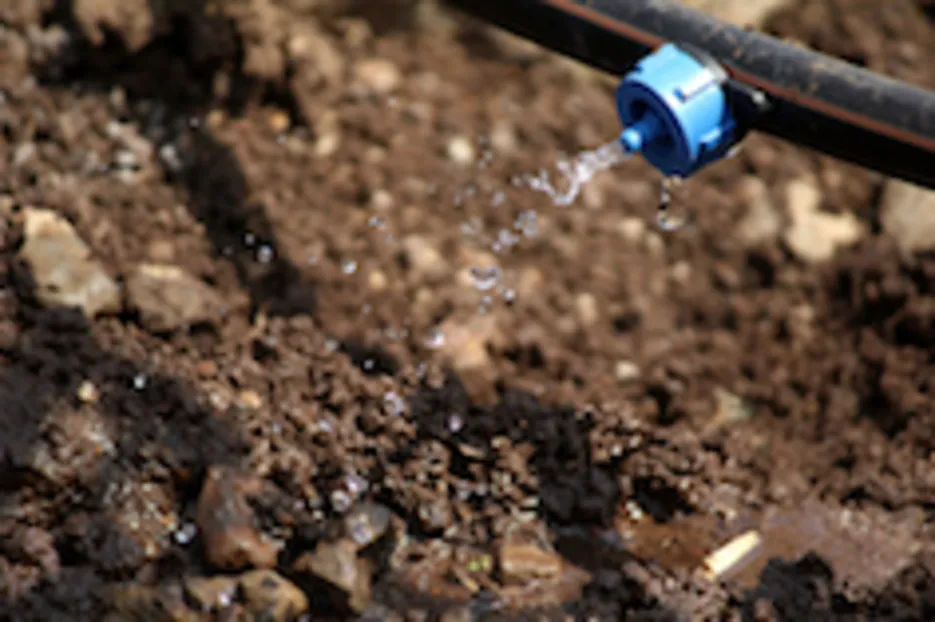

Fertigation means providing fertilizer to the crops by dissolving with irrigation water. Drip irrigation or trickle irrigation is an economical and environment friendly technology for irrigation. Only the root zones of the plants are provided with water.
Water wastage through runoff or infiltration is prevented saving about 50% of irrigation water, fertilizer requirement can be reduced by about 70%. The extra portions of the soil between the rows or the plants do not receive water or fertilizer so the growth of weeds also reduces. Cost of labour decreases. These factors reduce the input cost of the crop. Fertigation is best for the water scarce, undulated and less fertile soils. Pollution of the soil or the underground water due to leaching of excess fertilizer salts is prevented. Upto 23% increase in yield of the crops has been observed by the use of this practice.
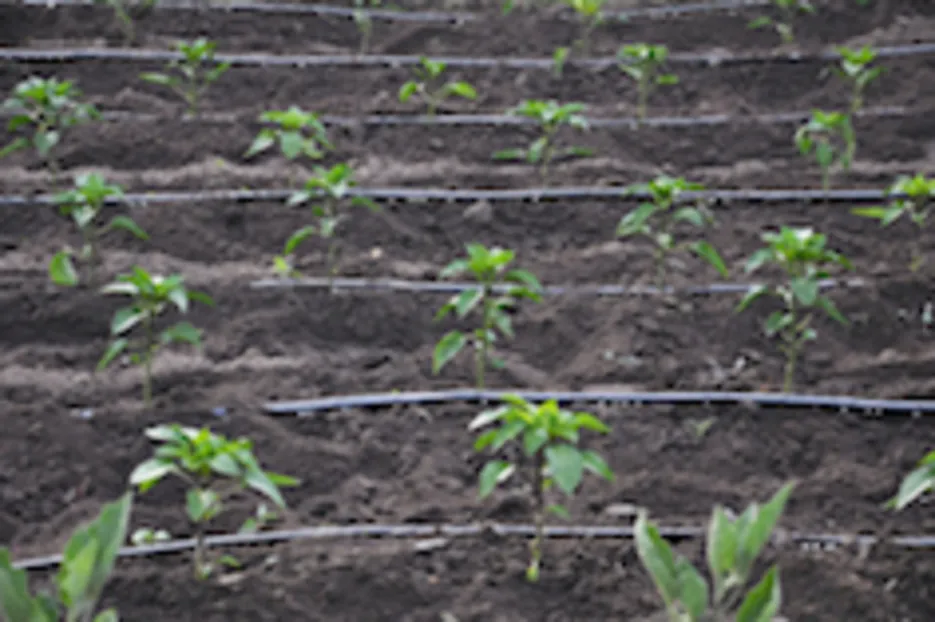



The system:
The system:
: Drip irrigation works through a network of pipelines- mains, sub-mains and laterals with emitters or drippers fitted at the ends near the root zone. Drippers release the water at a very slow rate of 2-20 litres per hour. The field can be irrigated anytime as per the requirement. The system consists of a control head which maintains the pressure and the rate of flow in the pipelines. In fertigation, the fertilizer tanks are connected to the control head.
_30117_1677490398.webp)

Cost of installation:
Cost of installation:
Initial installation cost depends on a number of factors, approximately in a crop with 1.2 m row to row spacing and 60 cm plant to plant spacing about ₹ 60,000 to ₹ 70,000 per acre can be required. In closed spacing crops, the installation cost increases. Financial assistance is readily provided by the government under “PMKSY- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana”. A component of this scheme is “Micro-irrigation- Per Drop More Crop”. Farmers can contact their District Horticulture Departments to take the benefits. Once installed, the set up works for about 20 years.
Precautions:
Precautions:
The diameter of drippers is very small 0.2 – 2 mm so the water should be free of any sediments, algae, microorganisms etc. to avoid any blockage. Fertilizers should be water soluble. Source of Nitrogen is Urea mainly as it is easily soluble in water. Ammonium sulphate should be avoided as it precipitates sulphate salts. For phosphorus, liquid phosphoric acid is used, Super Phosphate should never be used as it reacts with salts of water and precipitates phosphate salts.
Micronutrients and the phosphatic fertilizers should be kept in separate tanks to avoid their interactions and precipitation of salts. Potassic fertilizers are generally soluble in water. For micronutrients use chelated forms. In this case, the micronutrient like calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, or copper is coated with some organic molecule like EDTA which prevents its reaction with other salts in water and avoids clogging. Pipes are cleaned periodically with acid or chlorine flushing. Plastic pipeline system should be buried under the soil to prevent rat damage and direct solar radiation