 Back
Back

1. Nitrogen Deficiency
- Nitrogen Deficiency
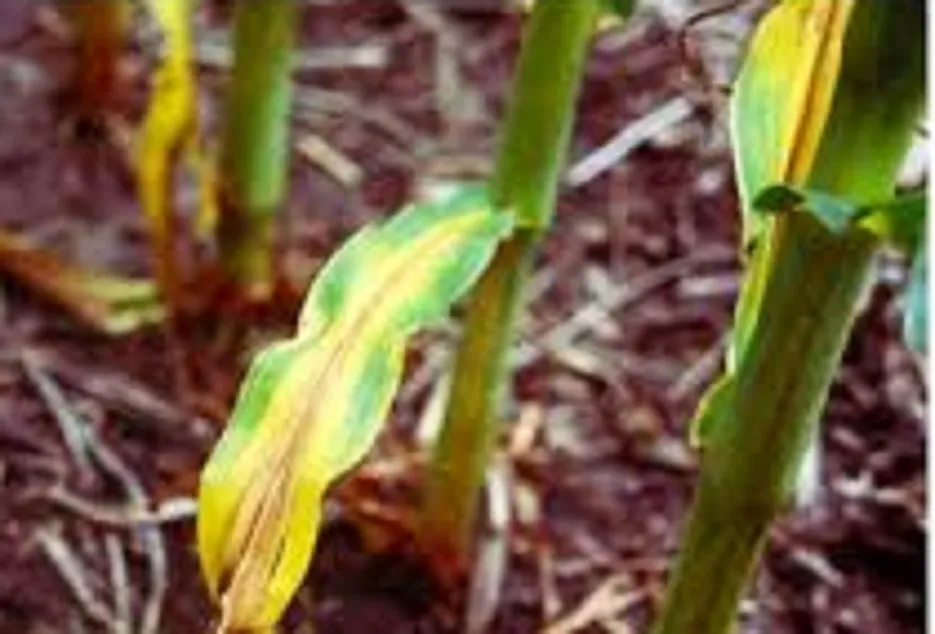
Symptoms If Nitrogen deficiency is there, symptoms are seen first in the lower leaves. The lower old leaves turn a pale or yellowish-green color. Discoloration starts at the tip of the leaf and extends toward the leaf base. The plants may be thin and stunted in growth.



Management
Management
• Spray 2% Urea solution (20 grams of Urea/liter of water) for immediate recovery from Nitrogen deficiency. • And soil application of fertilizer containing Nitrogen like Urea gives permanent recovery.
2. Potassium Deficiency
- Potassium Deficiency
Symptoms If Potassium deficiency is there, the symptoms begin on the older leaves and progress to the younger ones as the disorder becomes increasingly more severe. Leaf edges or margins become yellow and brown in color.
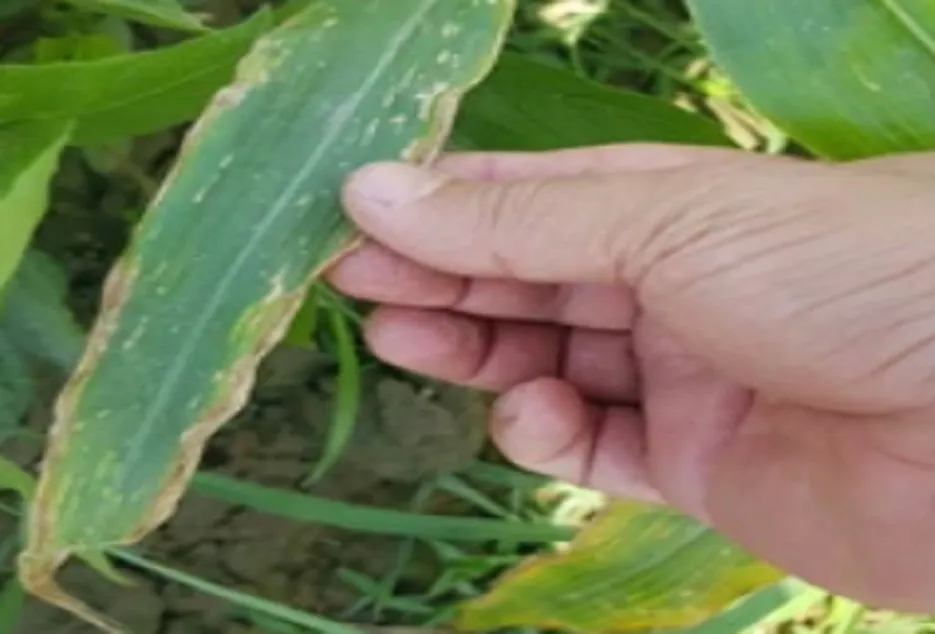


Management
Management
• For immediate recovery spray 1% Potassium Chloride (KCL) solution or 1% NPK(00:00:62) solution (10 grams /liter of water) at the rate of 1 kilogram per Acre. • And soil application of Muriate of Potash (MOP)gives permanent recovery from deficiency symptoms.
3.Phosphorus Deficiency
3.Phosphorus Deficiency


Symptoms Due to Phosphorus deficiency, leaf margin, veins, and stem show a dull green color and grow slowly. The underside of the leaves eventually turns a reddish-purple. Older leaves are affected first. • And soil application of DAP fertilizer gives permanent recovery.
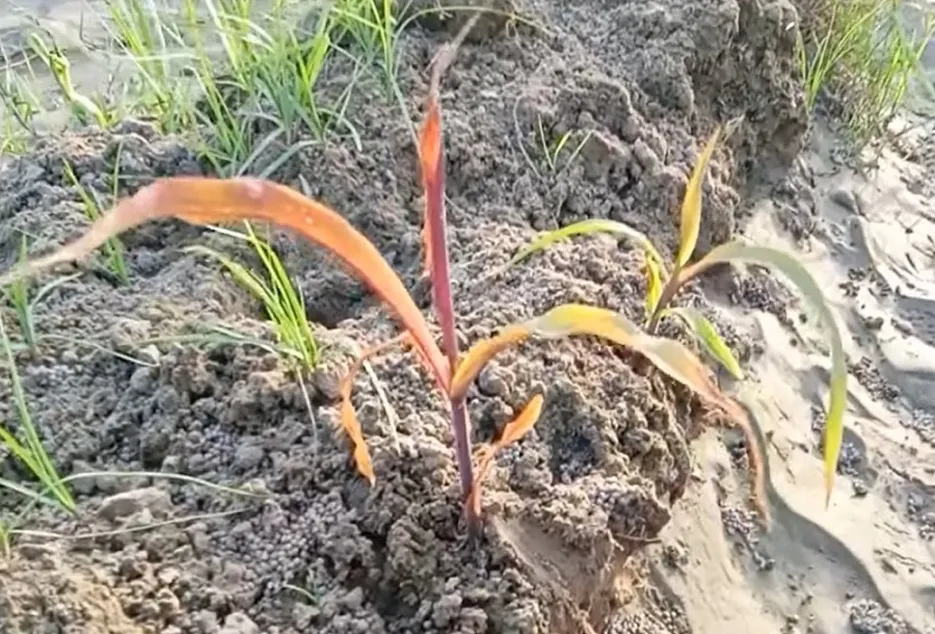


Management
Management
• For immediate recovery spray 2% DAP solution (2 kg of DAP is soaked for 24 hours in the water in a plastic container. After 24 hours this DAP mixture is sieved through a muslin cloth or through a nylon net and collected, in a plastic or earthen plot. This solution is sprayed by adding 100 liters of water to the crop.• And soil application of DAP fertilizer gives permanent recovery.


4. Zinc Deficiency
- Zinc Deficiency
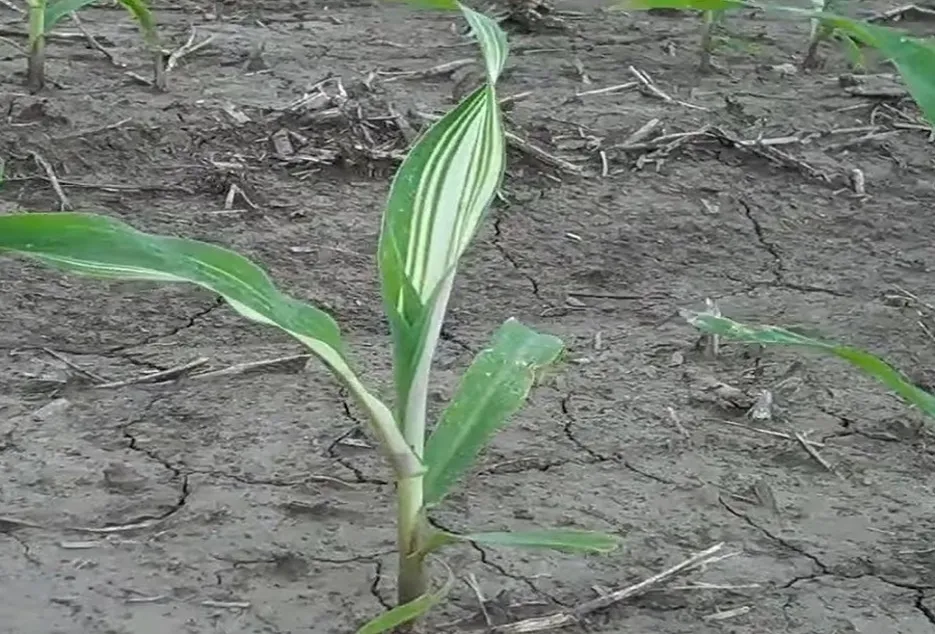


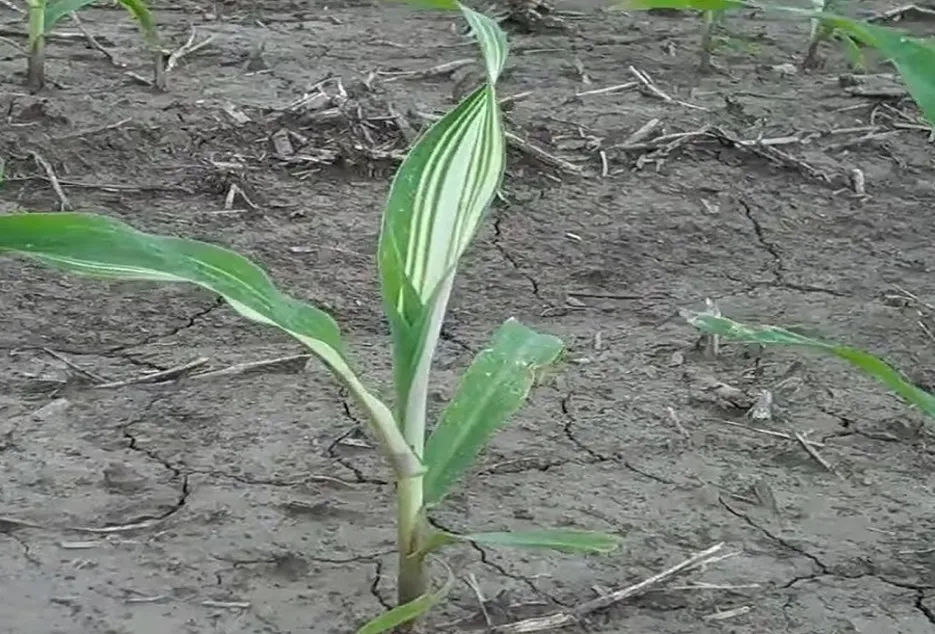
Symptoms Because of Zinc deficiency, Interveinal chlorosis on the upper leaves can occur with veins, midrib, and leaf edges remaining green and the older leaves exhibit orange-brown chlorosis.


Management
Management
• For immediate recovery spray 0.5% Zinc sulphate (5 grams /liter of water) or Chelated Zinc (Zn EDTA 33%) at the rate of 300 grams per Acre. • And soil application of Zinc Sulphate 10 kilograms per acre gives permanent recovery.


5. Boron Deficiency
- Boron Deficiency
Symptoms Boron symptoms are expressed as a shortening of internodes and death of growing points. Lack of boron will also result in poor pollination and reduce yields.
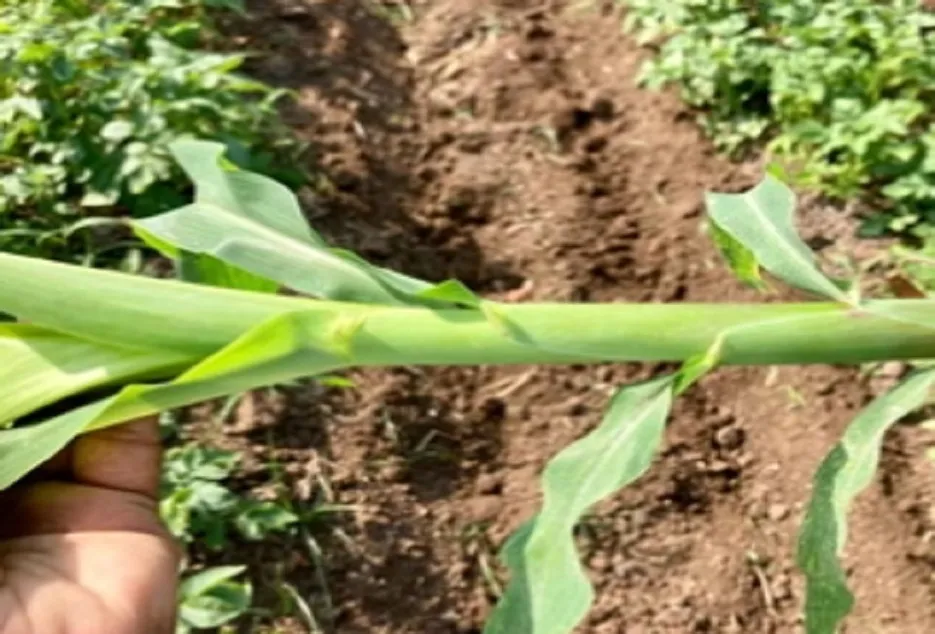


Management
Management
• For immediate recovery from deficiency symptoms spray 0.25% Borax (2.5 grams /liter of water) and repeat the spray at 15 days intervals. • And soil application of Multi-micronutrient fertilizer containing Boron gives permanent recovery.
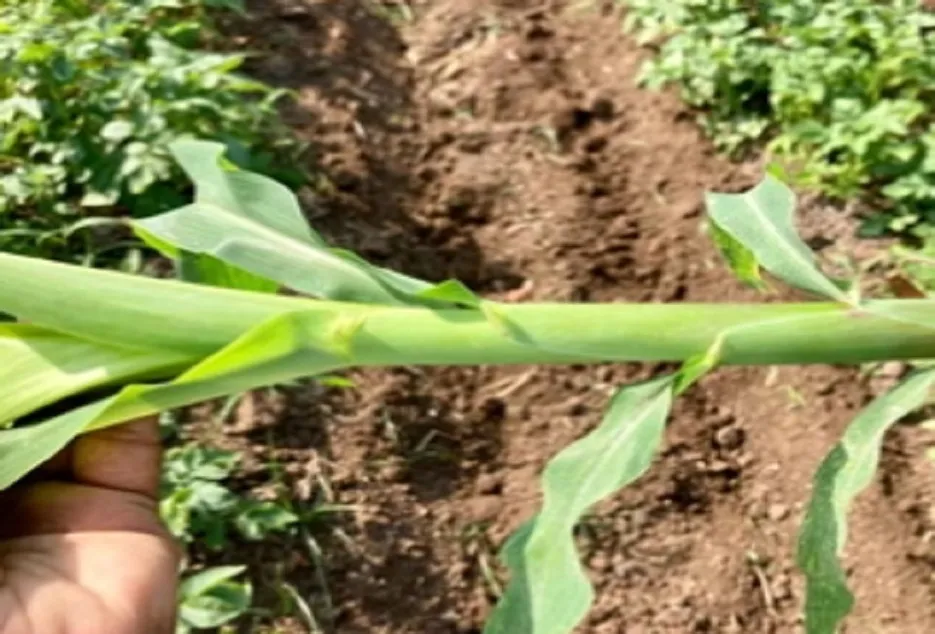


6. Calcium Deficiency
- Calcium Deficiency
Symptoms Due to Calcium deficiency, Interveinal chlorosis, and leaf margin necrosis occur at the growing point, which eventually dies. In crops like tomatoes, it causes blossom-end rot on fruit, this can be identified by the leathery scar on the blossom end of the fruit and the rotting of fruit along with the Flower drop.


_9335_1677489909.webp)

Management
Management
• For immediate recovery from deficiency symptoms spray Calcium Nitrate 5 grams/liter of water and repeat the spray at 15 days intervals.
• And soil application of Calcium Nitrate 10 kilograms per acre will help to fulfill the calcium requirement. Calcium Nitrate should be separately applied and should not be mixed with other fertilizers.


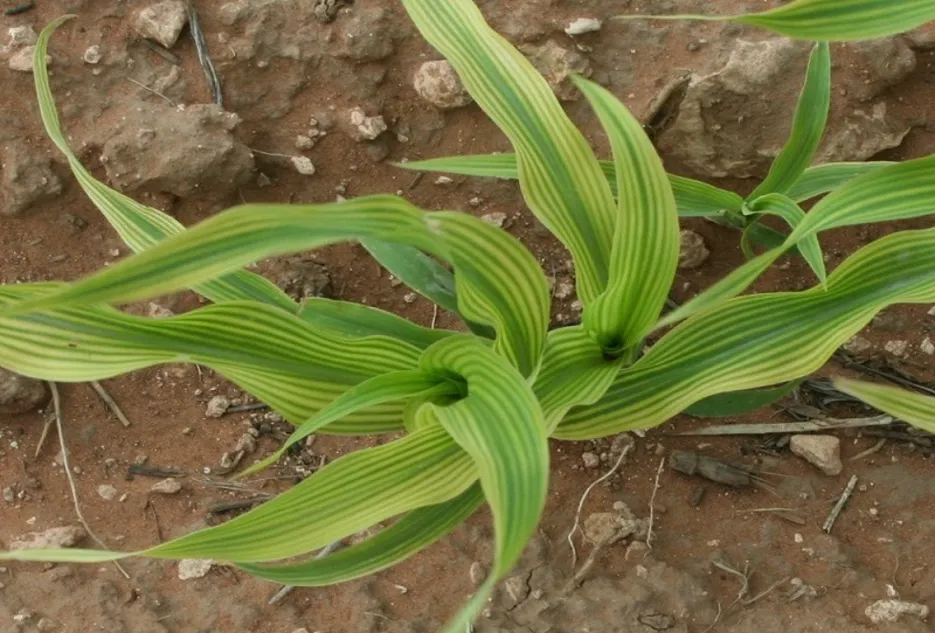
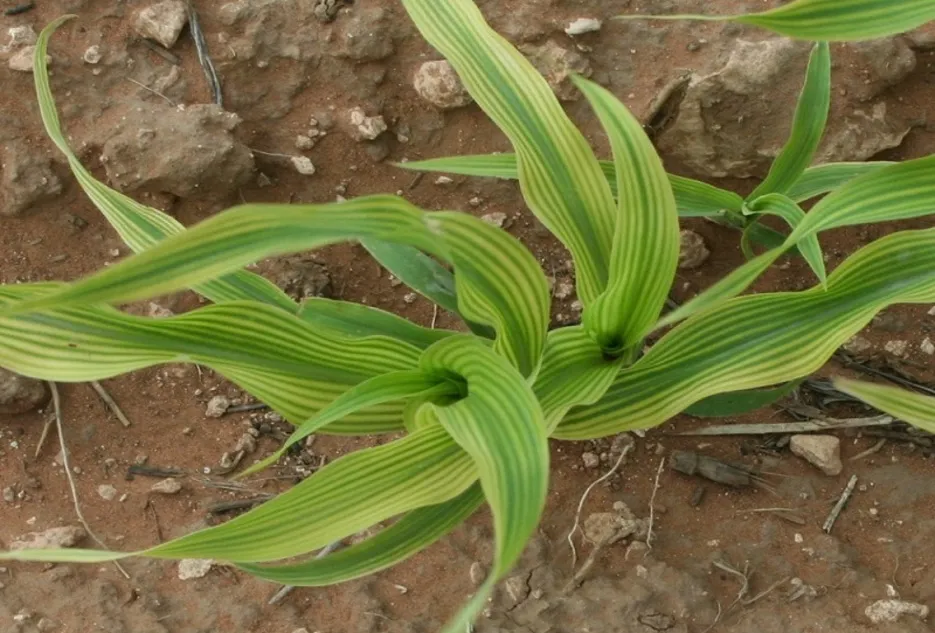
7. Iron Deficiency
- Iron Deficiency
Due to Iron deficiency, in the initial stages, interveinal areas of leaves turn yellow with veins green in color. When the deficiency becomes severe the veins also become yellow and chlorotic and the plant growth becomes stunted.


Management
Management
• For immediate recovery spray Ferrous Sulphate 5 grams/liter of water and repeat the spray at 15 days intervals. or spray Chelated Ferrous (Fe EDTA 12%) 150 grams per Acre in 150 liters of water. • And soil application of Ferrous Sulphate 12 kilograms per acre gives permanent recovery.


8. Sulphur Deficiency
- Sulphur Deficiency
Symptoms Sulphur deficiency symptoms start in the younger leaves, and they turn light green, the stems and petioles may turn purple and become spindly.
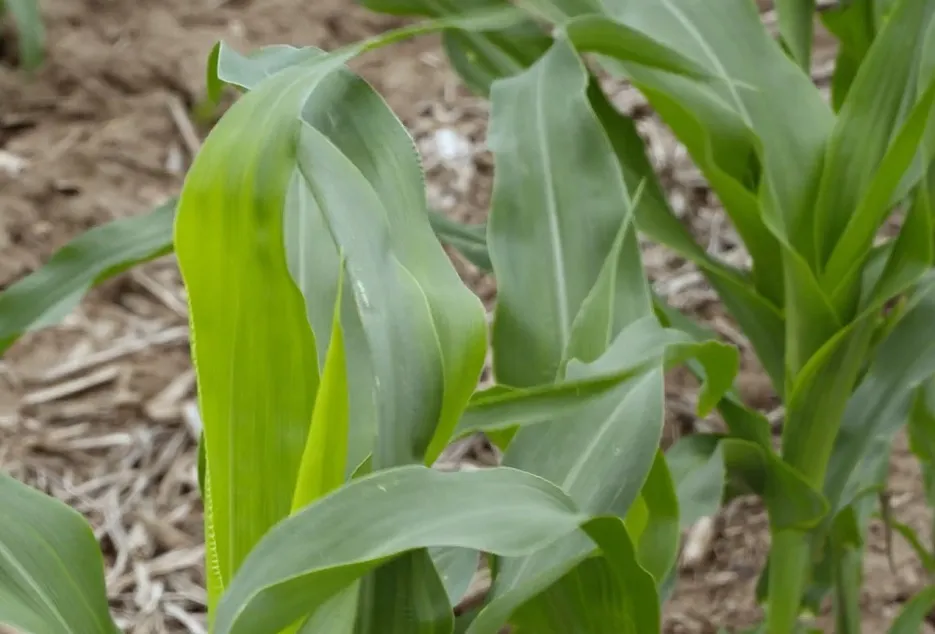
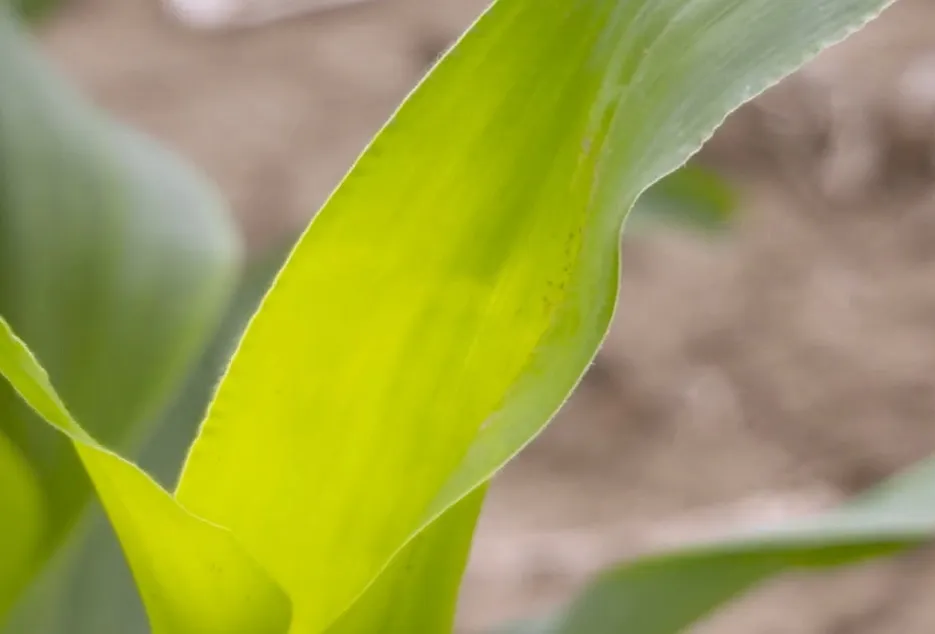


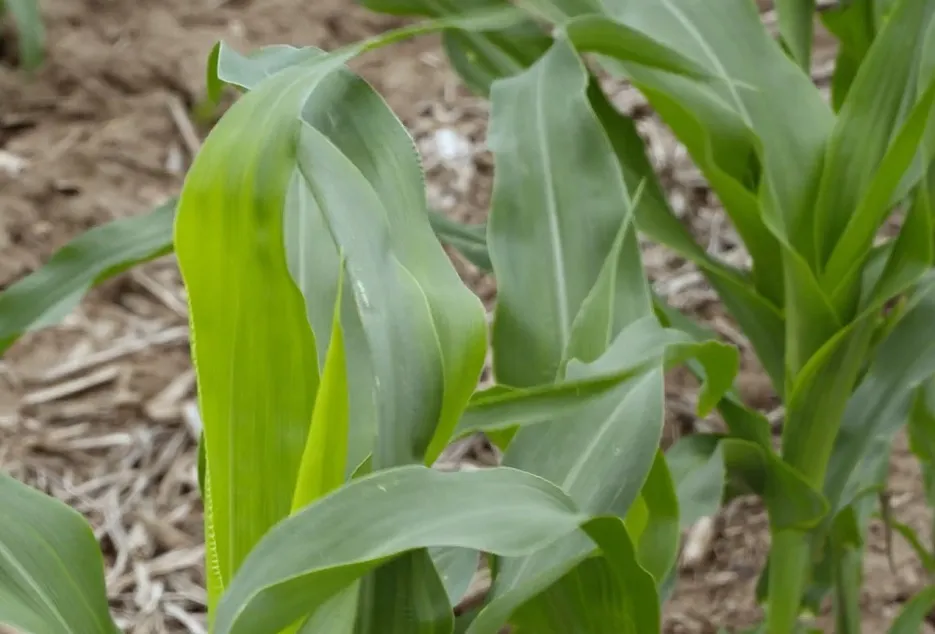
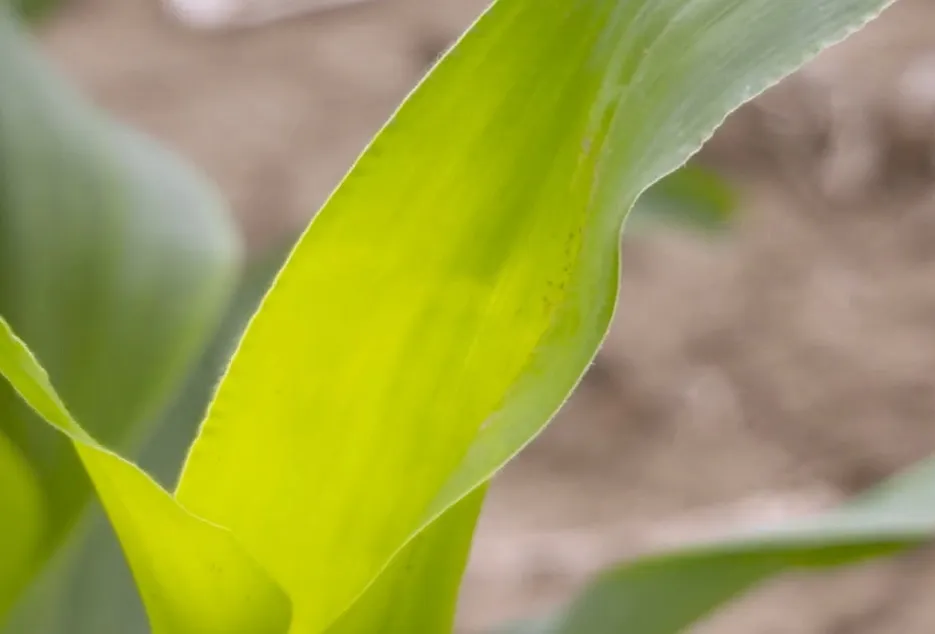
9. Manganese Deficiency
- Manganese Deficiency
Due to Manganese deficiency Necrosis occurs on the older or younger leaves. Fruit or cob development is affected.
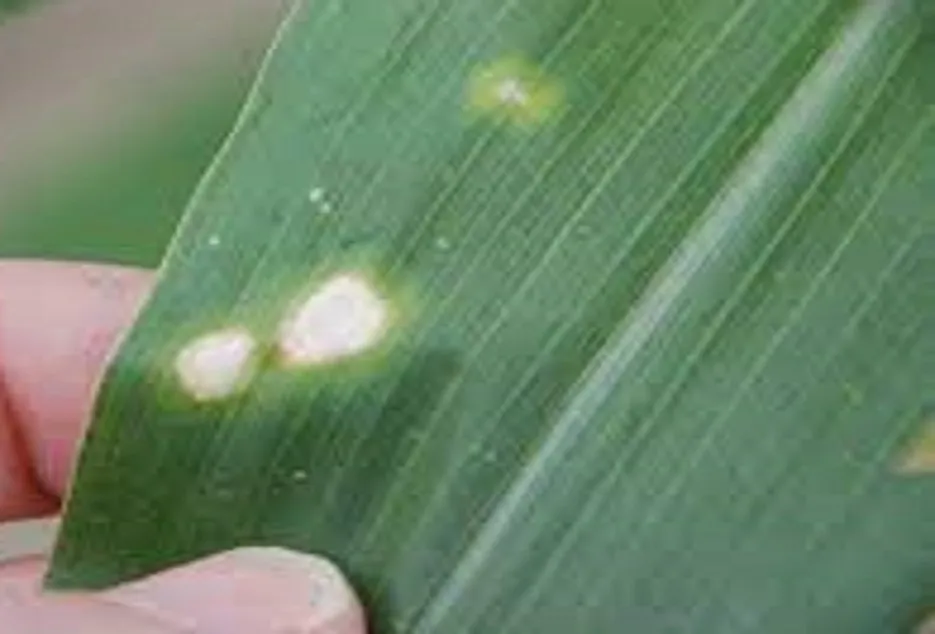




10. Magnesium Deficiency
- Magnesium Deficiency
Leaves develop interveinal chlorosis, starting on the older and progressing to the younger leaves. The midrib of the leaf remains green while the interveinal tissue becomes necrotic.
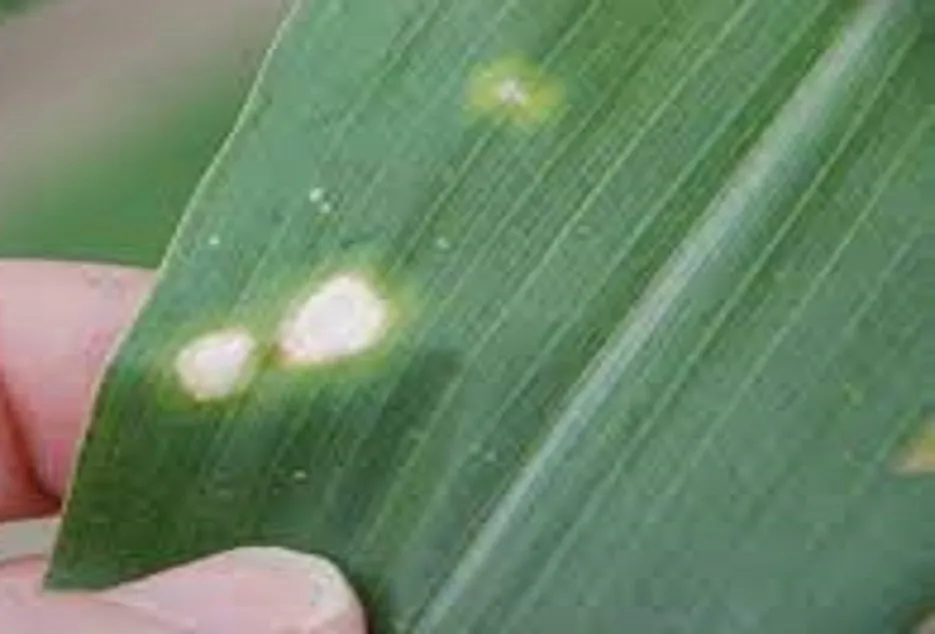




11. Copper Deficiency
- Copper Deficiency
Initially, the younger leaves wilt and then may turn bluish-green and curl upwards. Severely affected plants are stunted and chlorotic.


Management practices for Sulphur, Manganese, Magnesium, Copper
Management practices for Sulphur, Manganese, Magnesium, Copper
• Spray micronutrient mixture containing all essential nutrients like Zinc, Magnesium, Calcium, Sulphur, Iron, Copper, Boron, Manganese & Molybdenum.


Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!