 ପଛକୁ
ପଛକୁ
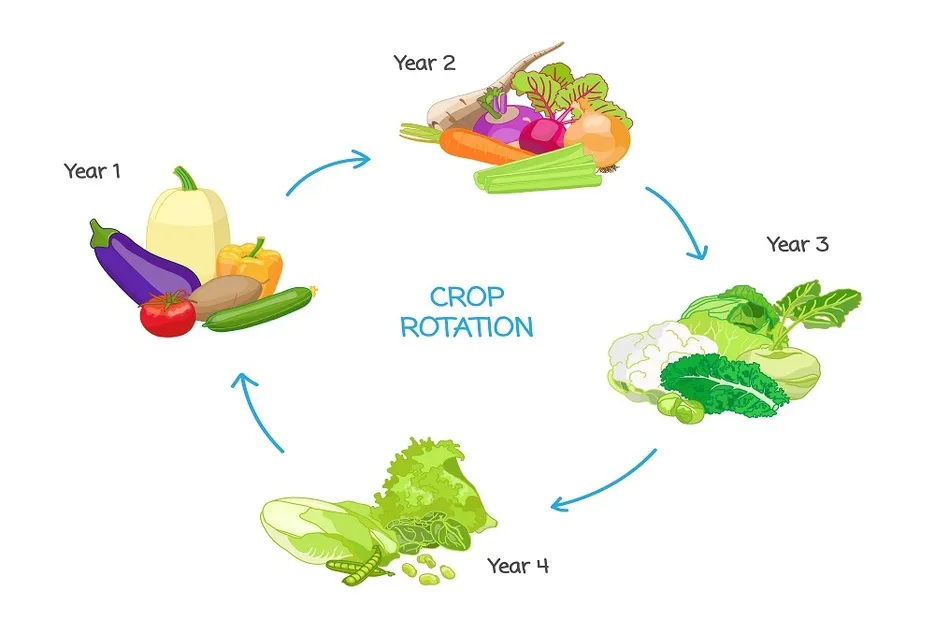
Are you facing frequent diseases like wilt and other leaf spots in your crop? Crop rotation might help to reduce the incidence of major diseases. Crop rotation is also an important strategy for managing weeds, and insect pests of vegetable and field crops. Rotating crops also provides nutritional benefits to plants and maintains soil health.ADVANTAGES OF CROP ROTATION:-
Disease Management
Disease Management
Vegetables belonging to the same family can be considered as a rotational group because they are susceptible to many of the same diseases and insect pests, share similar nutrient requirements. The populations of these types of diseases may not decline if the same crop is grown . But crop rotation can help to keep the diseases under control by slowing their development.
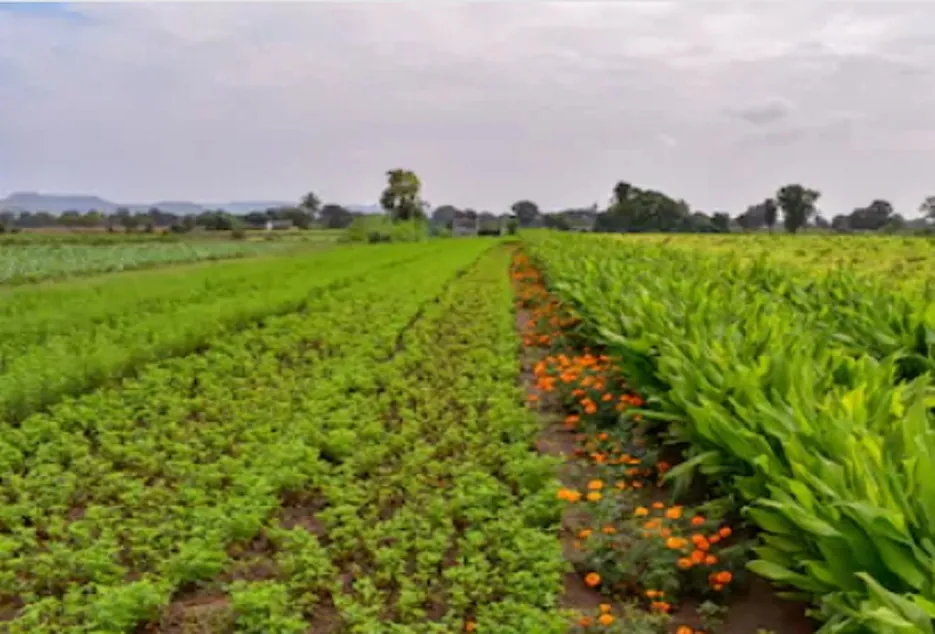


Nematode Management
Nematode Management
Many plant pathogenic nematodes are soilborne and can be managed with crop rotation. Nematodes, like root-knot nematodes, have wide host ranges. For nematode problems, it is important to correctly identify the causal agent and to rotate to non-host crops for the amount of time needed to sufficiently reduce the nematode populations.


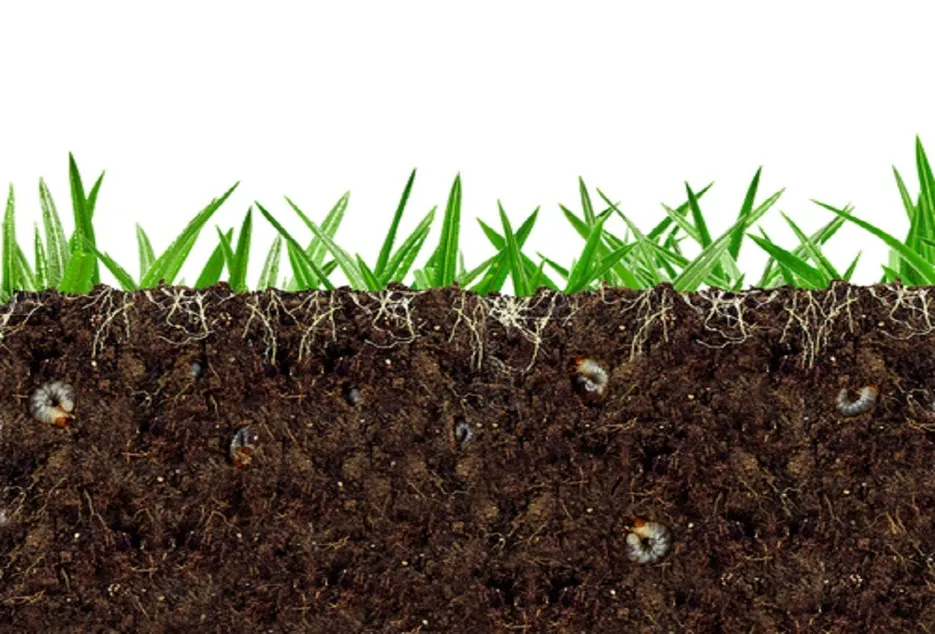
Insect Management
Insect Management
Crop rotation can be used to break the life cycle of insect pests. Most of the dormant stages of insects remain in soil and start damaging crops once planting is done. If the field is rotated to a non-host crop, the larvae do not have a host crop to feed on and they die, breaking the cycle. Breaking the life cycle of insects is an important management practice for pink bollworm as well which has become a major problem in cotton these days.

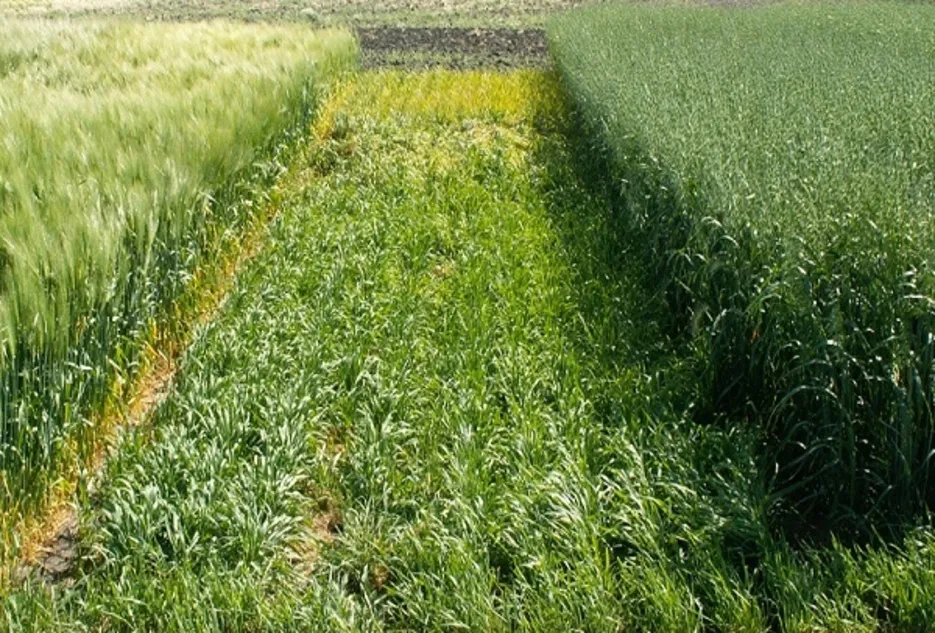
Weed Management
Weed Management
Crop rotation can also be used to help manage weed problems because different crops compete with different weed species. Crop rotation also prevents the buildup of a few species which has become major weeds due to continuous cultivation. This practice also reduces the prevalence of problem weeds that can build up over time.
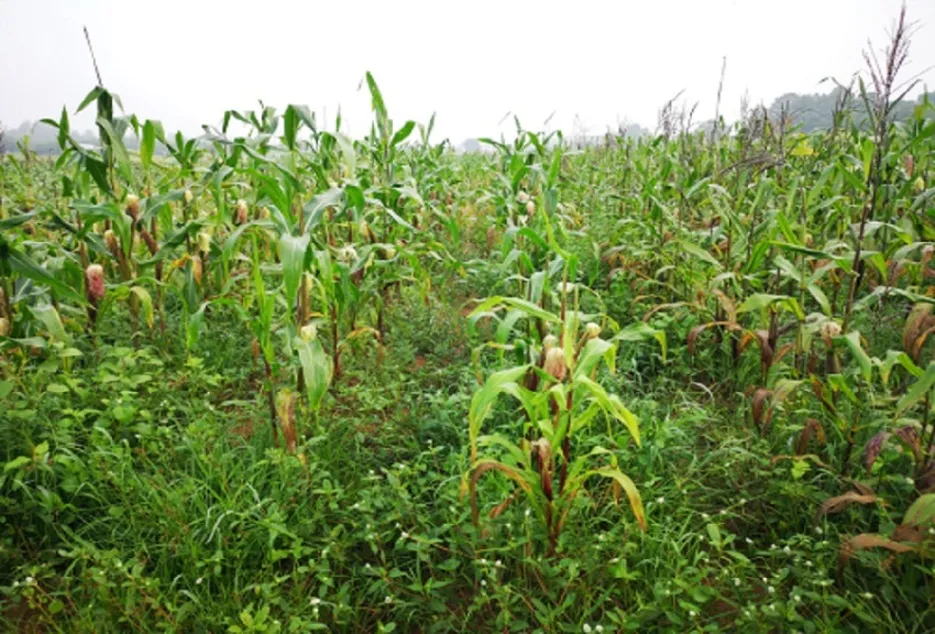


Nutrient Use
Nutrient Use
Crops differ in their nutrient requirements and their abilities to extract nutrients from the soil. Legumes like pulse crops can fix atmospheric nitrogen and be used to increase soil nitrogen levels.


Below are the crops belong to same family to be alternated with other family crops
Below are the crops belong to same family to be alternated with other family crops
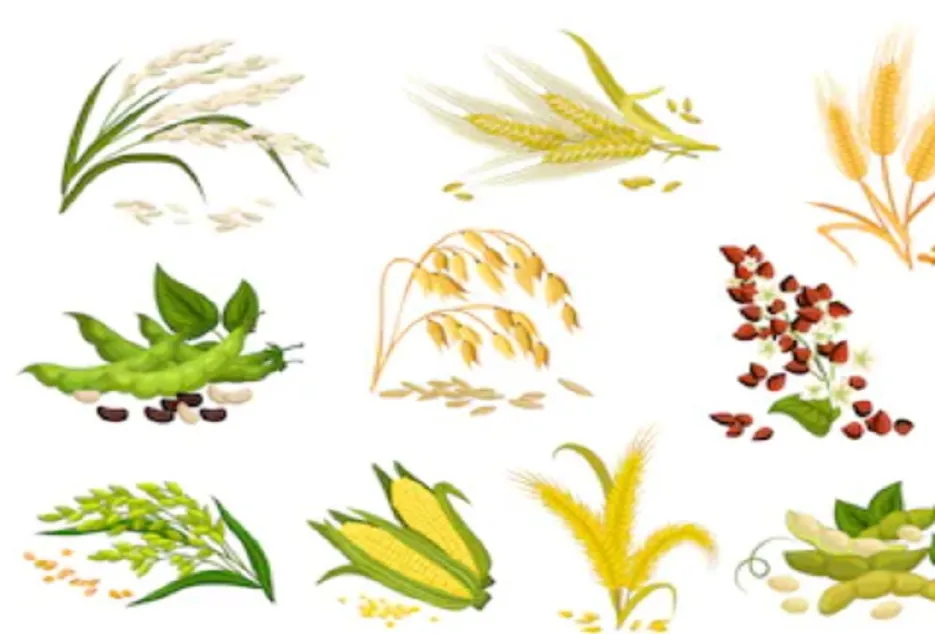
Grass Family
Grass Family
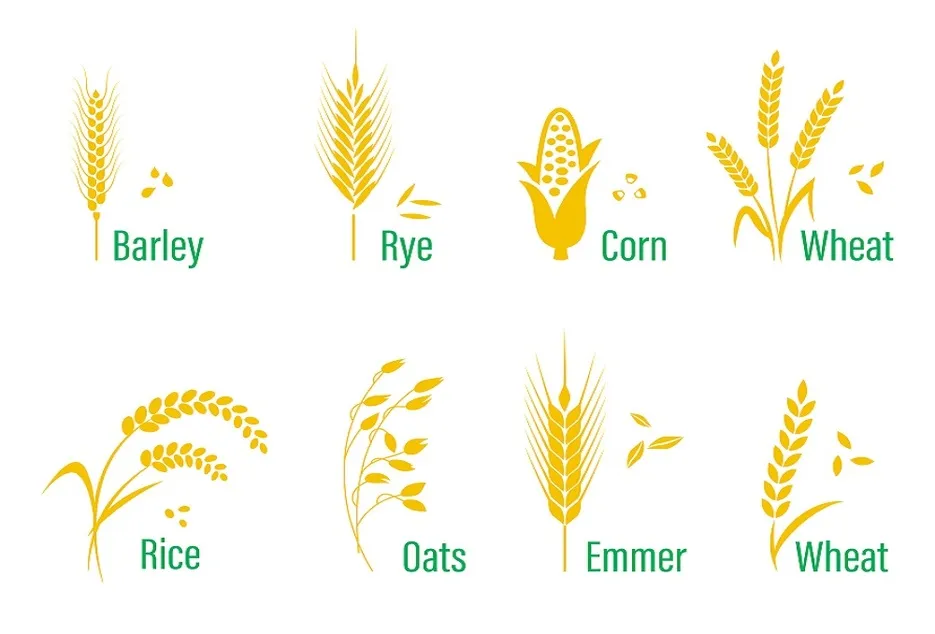


Grain crops like rice, wheat , Maize . Rotate these crops with members of the tomato or Solanaceae family.
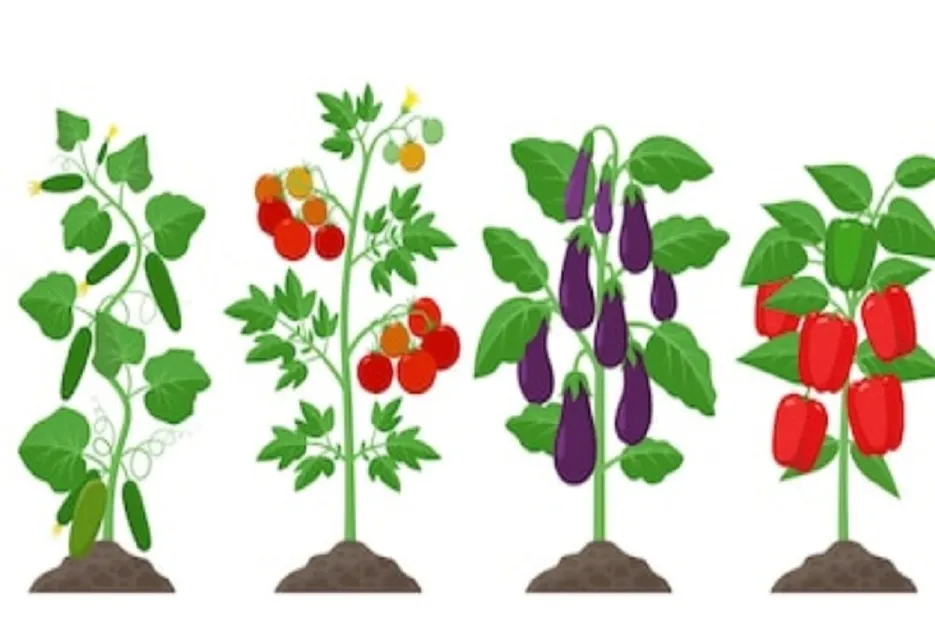
Tomato Family
Tomato Family
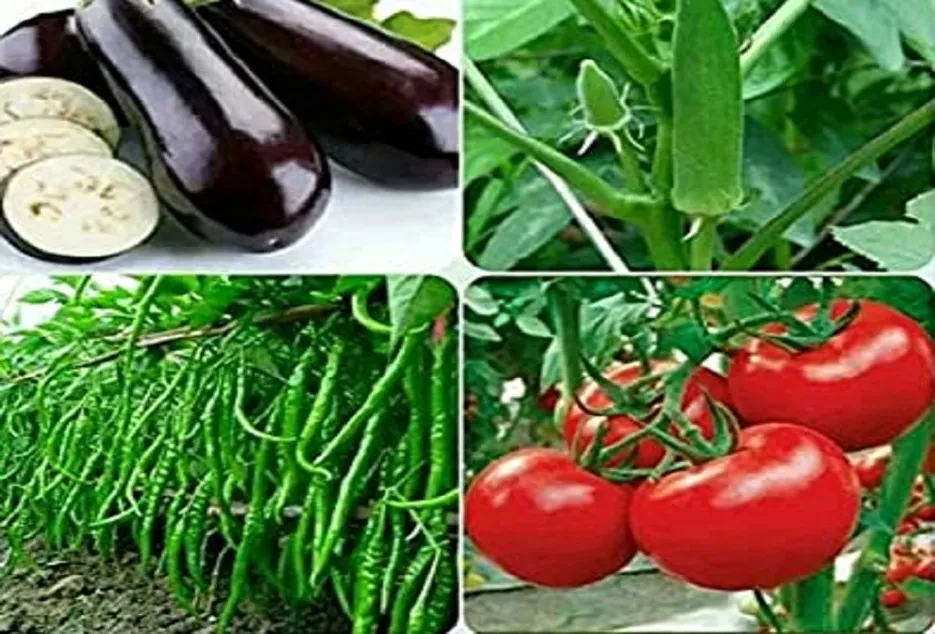


Brinjal , Chilli , Tomatoes, Potatoes. These crops uptake fertilizers . Plant these crops after members of the grass family. Rotate these crops with legumes.
Cabbage Family
Cabbage Family
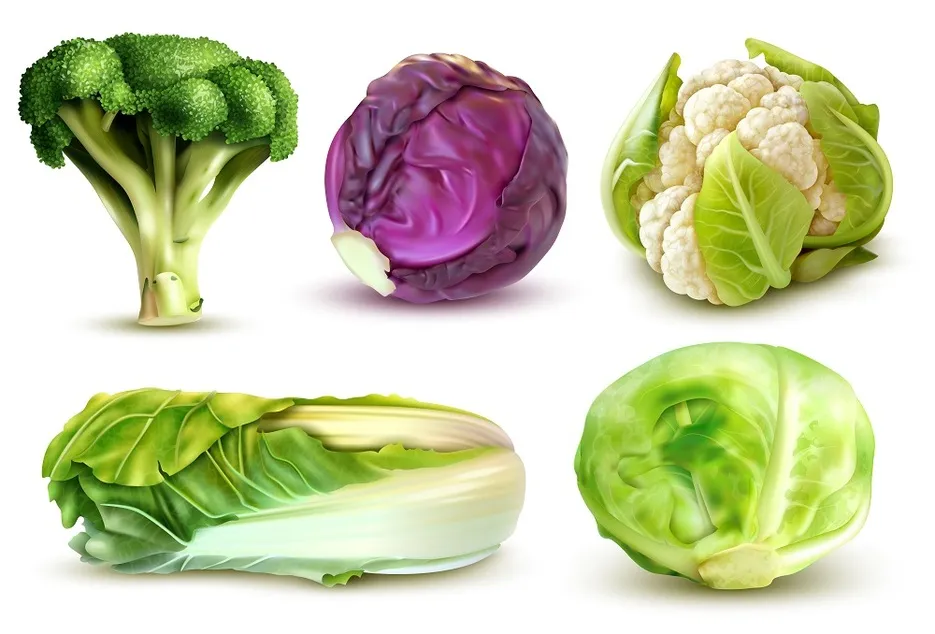


Cabbage, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage,Broccoli, Brussels sprouts radishes, turnips. These are heavy feeders. These crops should follow legumes. After these crops allow the garden add plenty of compost and organic matter to the field
Carrot Family
Carrot Family

Carrots, celery, coriander, parsley. These are light to medium feeders. These crops can follow any other group. Follow these crops with legumes, onions, or let the garden sit fallow for a season
Cucurbit Family
Cucurbit Family
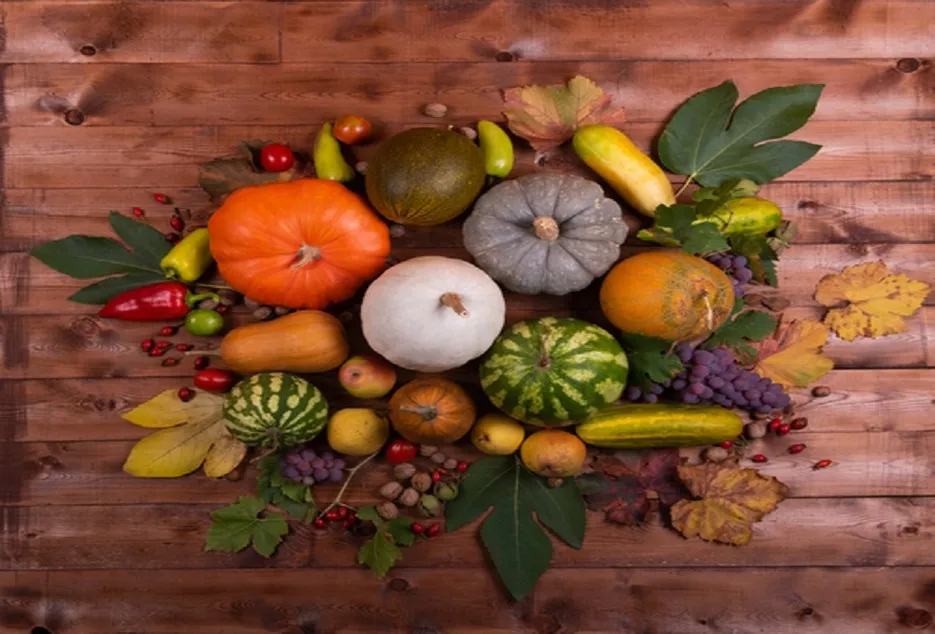


Cucumbers, melons, squash, pumpkins, watermelon. These crops are heavy feeders. Plant these crops after members of the grass family. Follow these crops with legumes.
Onion Family
Onion Family
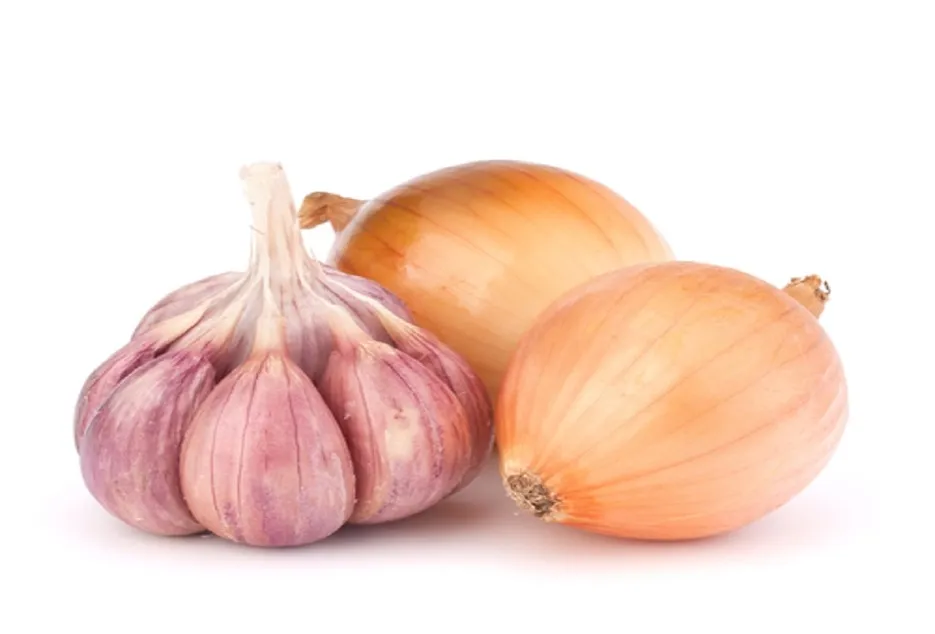


Garlic, onions, These are light feeders. Plant these after heavy feeders or after soil enrichers such as beans.
Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!