 ପଛକୁ
ପଛକୁ

Care of rootstock
Care of rootstock
New growth on rootstock starts 10-15 days after planting. The plants can be maintained by adequate and frequent irrigation. Since the feeder roots are concentrated on the top layer of soil only frequent irrigation is required during this period.
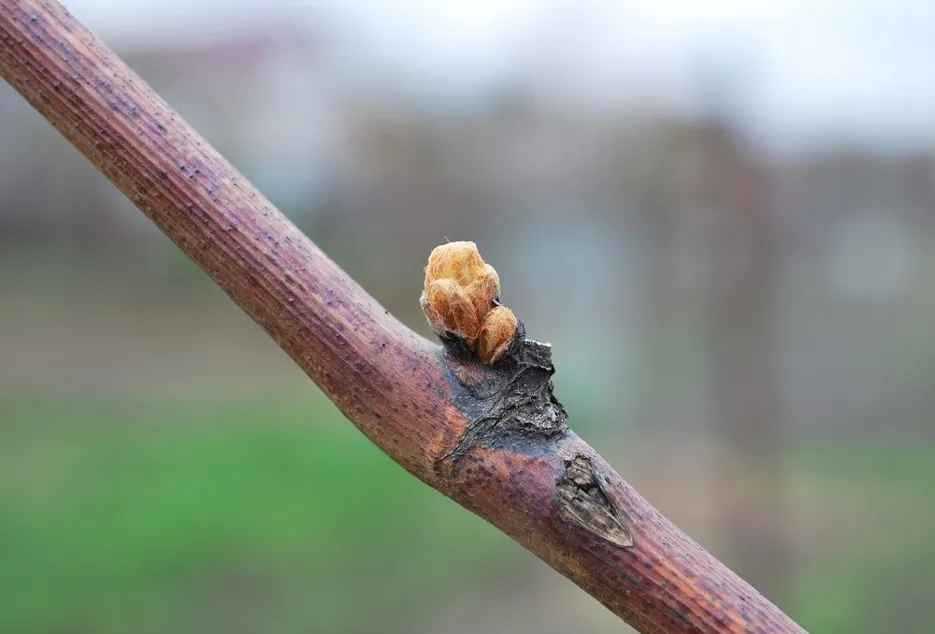
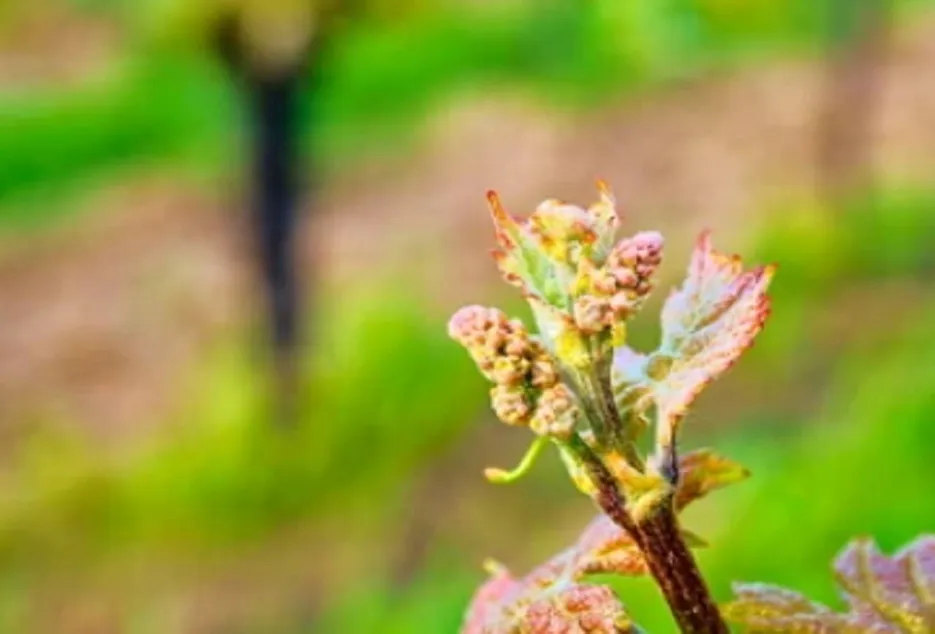



Pest and disease management of rootstock plants
Pest and disease management of rootstock plants
In general, rootstock plants do not get affected by diseases like those on popular commercial varieties except rust, which is a major problem. The incidence is observed after 3 months of planting on mature leaf. The disease organism sucks the sap from old leaf making the attachment weak. Hence, care should be taken to control the rust by spraying fungicides Blue copper (2g/lit and Bavistin @ 1g/lit) at fortnightly intervals. In addition to the disease, the rootstock plant suffers with flea beetle incidence. Please spray recommended insecticide for managing flea beetle.
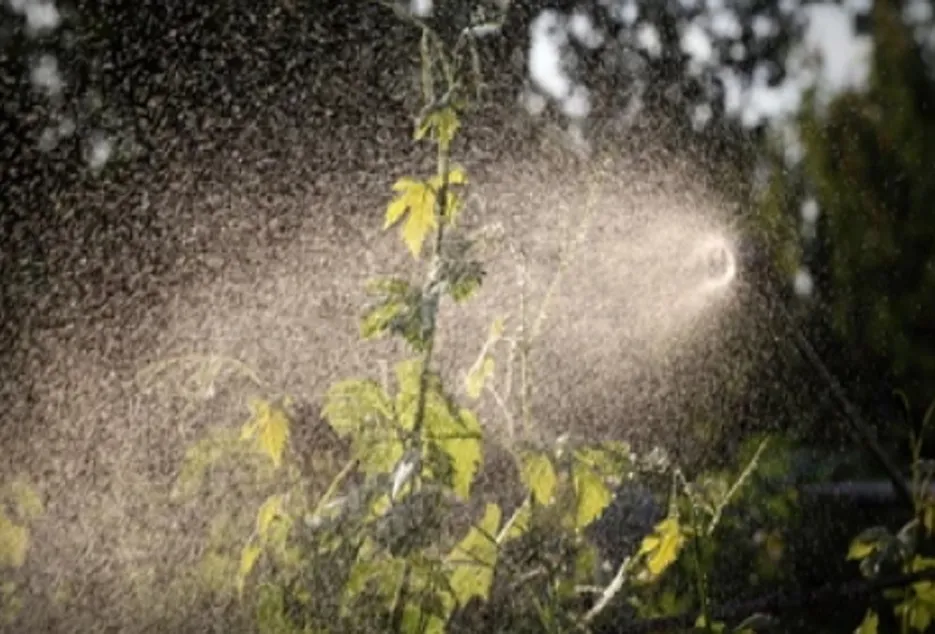
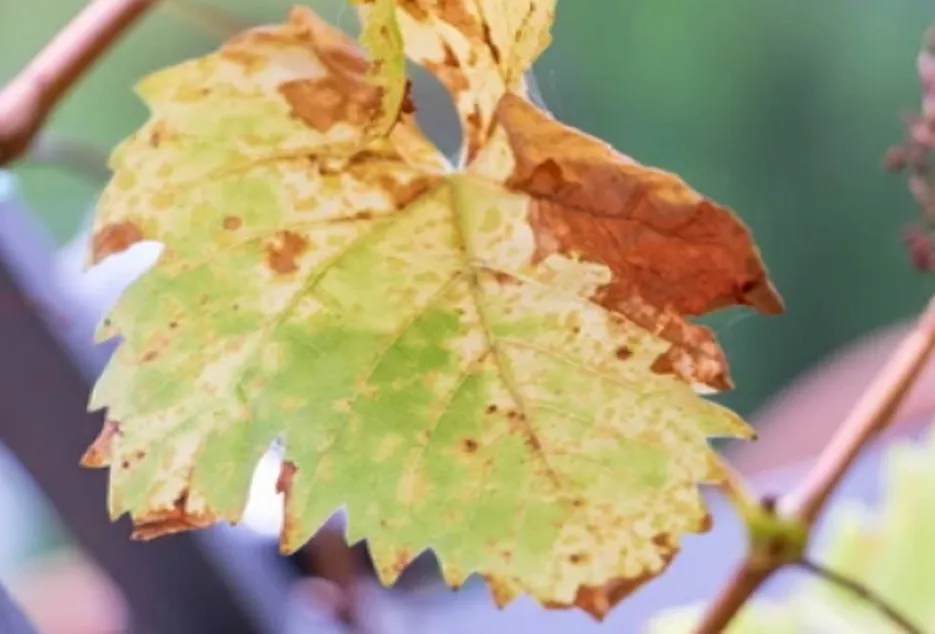


Re-cut of rootstock plants
Re-cut of rootstock plants
The growth of all the shoots of rootstock plants will not be uniform since the rootstock obtained from the nursery for planting will not be uniform. During the initial stage of vegetative growth, for proper root development all the shoots are also needs to be allowed to grow. This will maintain the balance between roots to shoot.
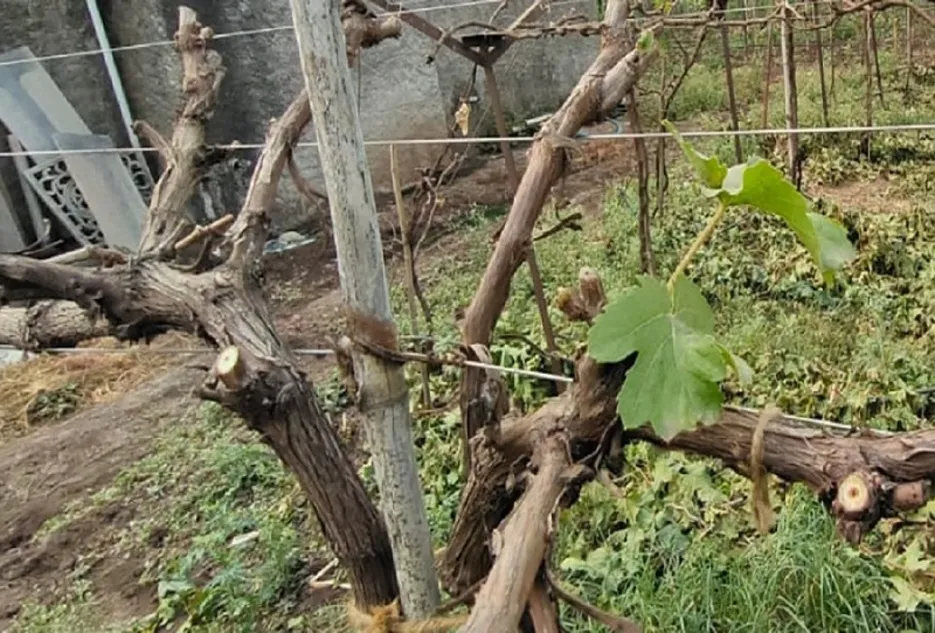


Training of new shoots
Training of new shoots
Once the re-cut of rootstock shoots is taken, there will be faster bud sprouts. There will be more than 5-6 shoots form each plant after re-cut. However, the grafting will be performed on two shoots only.
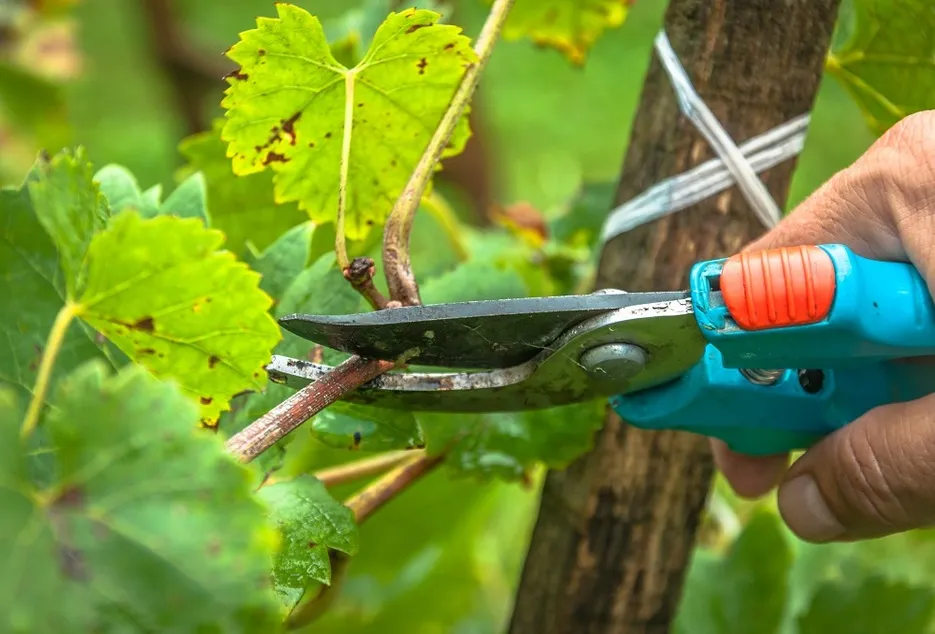




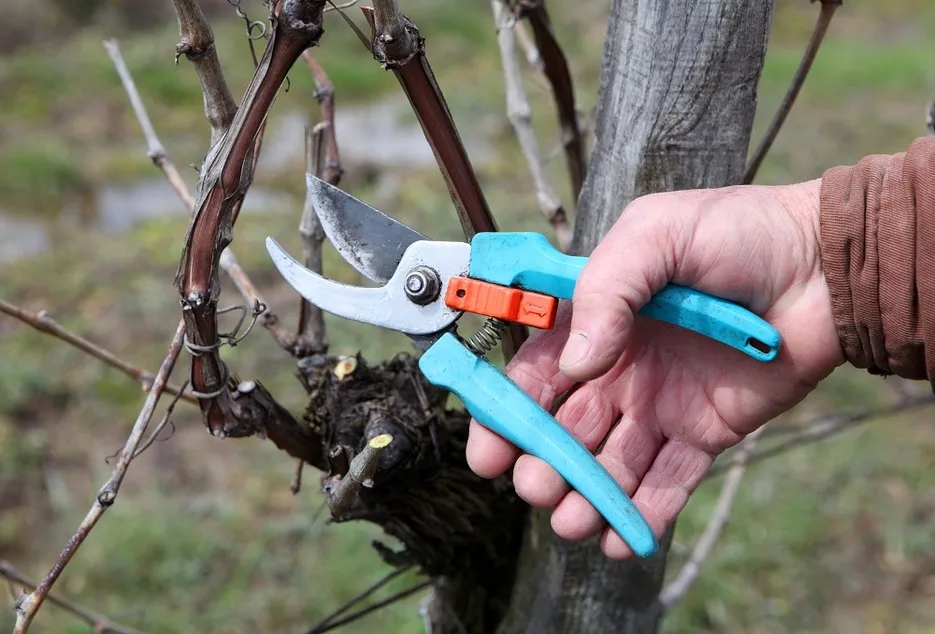
Grafting
Grafting
The rootstock planted during January-February will be ready for grafting during August-September. During this period the temperature in the atmosphere will be about 30 to 35°C while the relative humidity will be above 80% which is an ideal condition for graft success. The rootstock plants will be in active sap flow condition and hence, success of grafting is high during August last week to September last week.
Preparation of rootstock plants
Preparation of rootstock plants
The active sap flow condition of rootstock plants will help to achieve maximum grafting success. Sometimes, the required condition may not be available in the vineyard. Hence, irrigation 2-3 days before actual grafting may be given in the rootstock garden. The rootstock shoots are generally cut two feet above the ground for easy convenience of grafting.
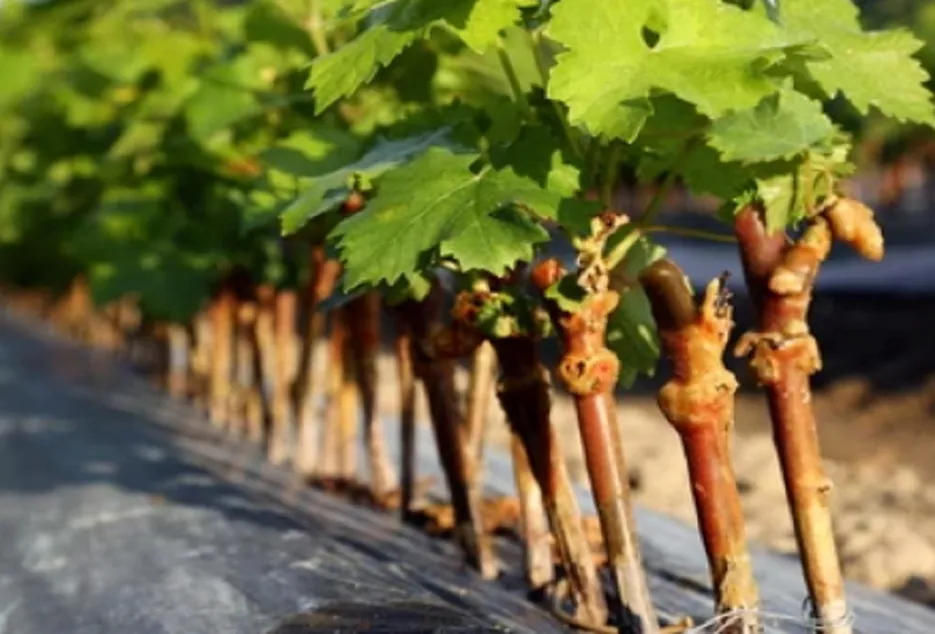


Preparation of scion
Preparation of scion
The scion stick selected for grafting should be from healthy, high yielding and disease-free vines. Generally, for grafting two bud sticks are used. The 2-bud cuttings prepared should be soaked in Bavistin @ 2 g/lit solution for about 2- 3 hours prior to grafting. This will help to control the major fungal diseases. Care should be taken that the cuttings selected for grafting should be completely matured.
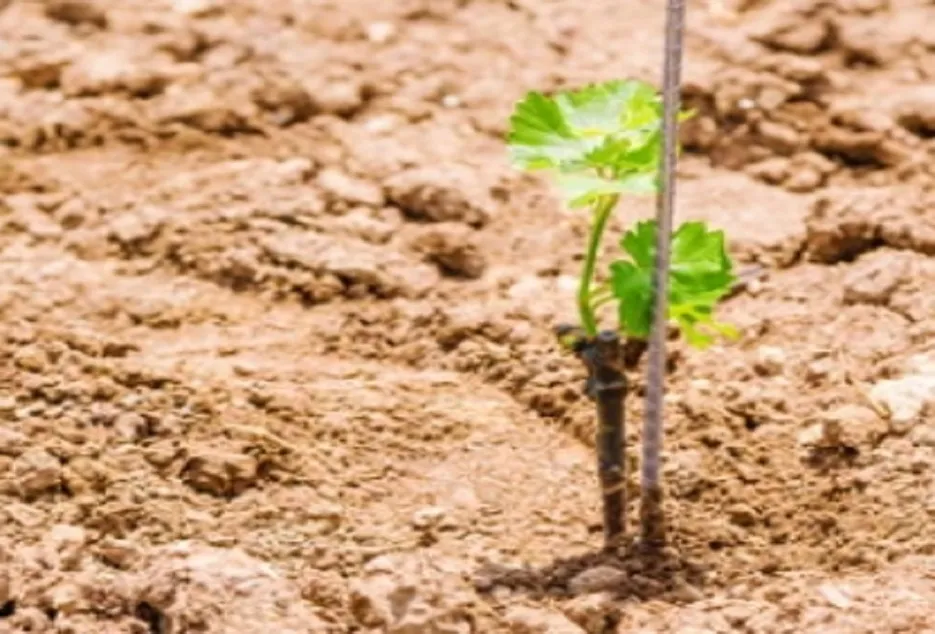
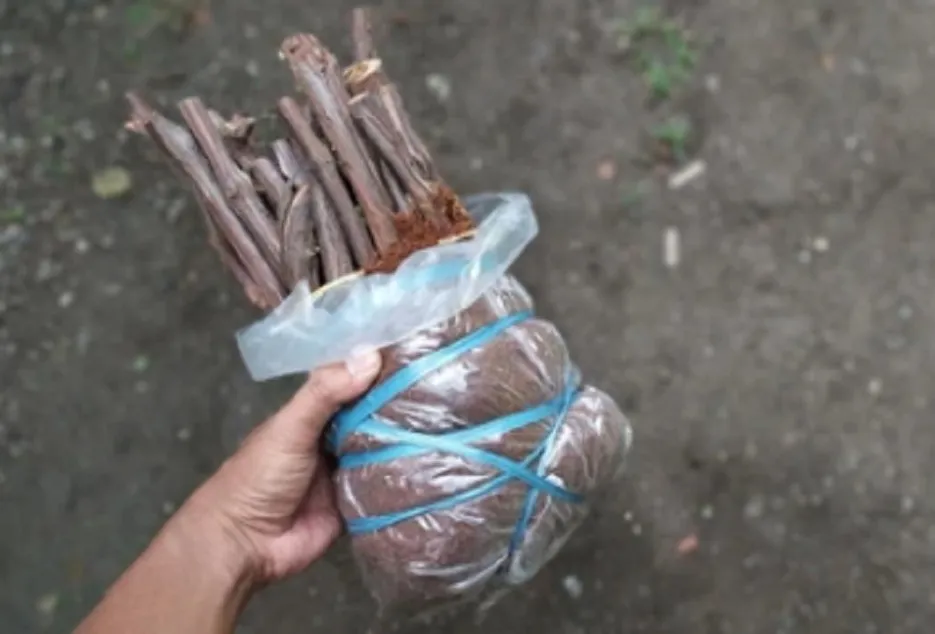




Grafting
Grafting
Grafting is a process in which a new grape vine is produced by making a cut in the rootstock and then adding scionwood that is cut to fit inside the incision made in the rootstock.
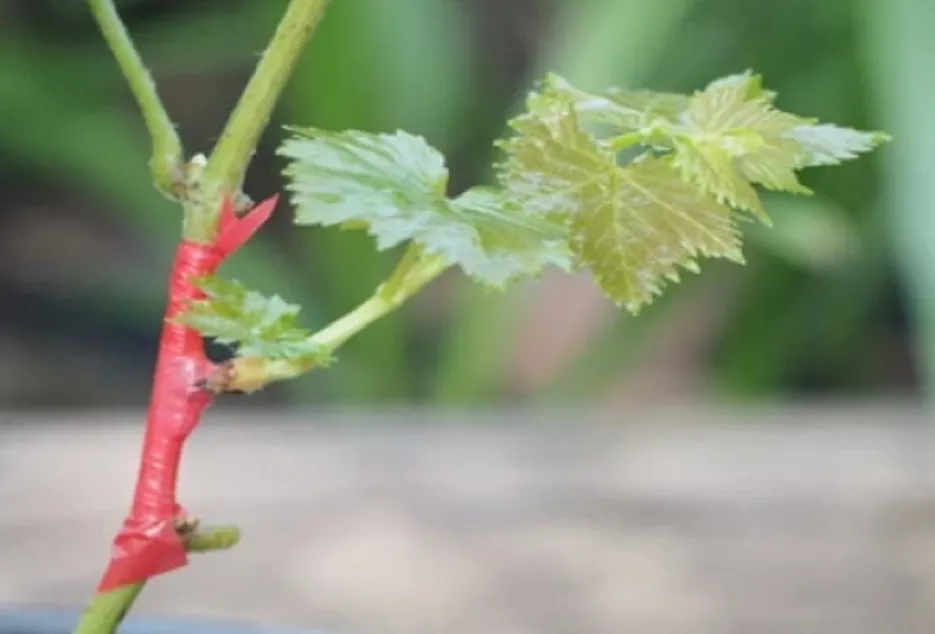
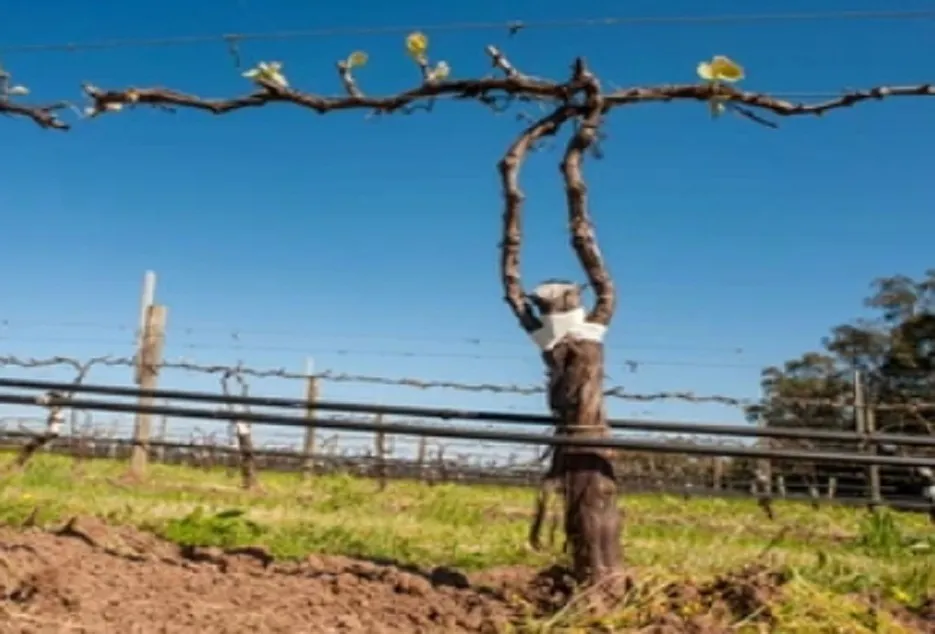


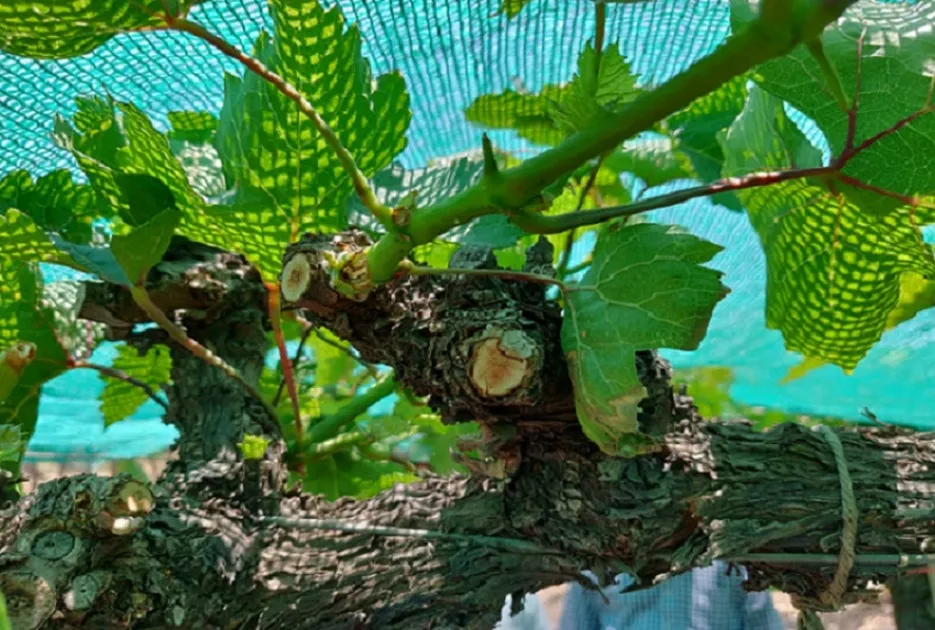
Care of grafted plants
Care of grafted plants
The bud swelling starts after 10-12 days of grafting while the bud sprouting starts 16- 17 days after the grafting. During the period of bud swelling, the attack of flea beetle becomes the major problem. The insect eats the bud completely leaving the dry and dead bud leading to complete failure of graft. Hence, during this period, spray of recommended insecticide will help to control the pest. If the he relative humidity in the atmosphere will be 90 to sometimes 100% due to rains and cloudy condition. During leaf emergence after bud sprouting, incidence of fungal diseases like downy mildew will be more. Hence, during the bud sprouting stage, spray of systemic fungicides followed by contact fungicides will help to keep the disease under control.


Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!