 ਵਾਪਸ
ਵਾਪਸ

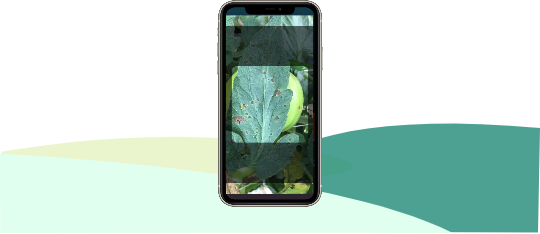
Pink bollworm (PBW) is a major pest of cotton and causes damage to lint and seeds. PBW larvae enter green bolls and feed on the developing seeds and also damage the lint. The stained lint and damaged seeds reduce the marketable quality causing economic loss to farmers and traders.
_82196_1677490060.webp)
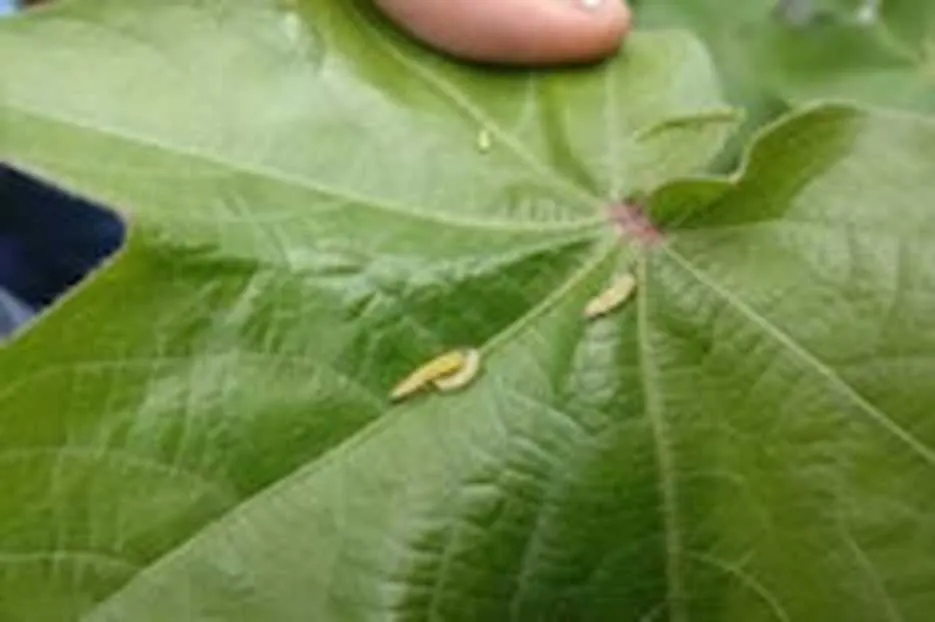

The mature larvae often go through a resting phase for several months within the damaged seed and thus get transported from PBW damaged fields to ginning mills. The resting larvae complete the cycle to emerge as moths when favourable conditions prevail in the following cotton growing season. Thus, seed-cotton with resting PBW larvae is a source of further spread to the next season and to newer areas. It is important to break the life cycle by destroying the resting PBW larvae in the cotton gins by adopting the following;
Pink bollworm management in cotton gins:
Pink bollworm management in cotton gins:
_51400_1677490062.webp)

- Do not store seed-cotton for long time. Complete ginning activities by April.
- Do not transport seed cotton damaged by PBW to other places for processing and oil extraction. This helps in the spread of PBW to these new places. Destroy PBW damaged seed-lots by burying them at the earliest.
- Damaged seed cotton should be sun dried by spreading thinly to kill live larvae and pupae.
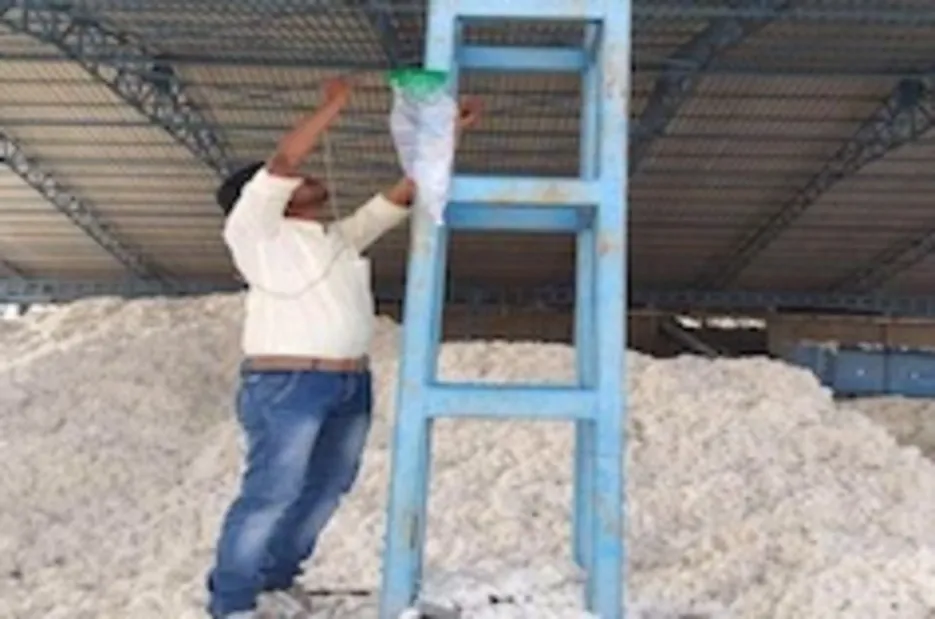
- Install PBW pheromone funnel traps during the ginning period (Nov-March). This prevents carryover of the pest to the following cotton crop around your gins. a. Install 20-25 traps in your mill around the area where seed-cotton and trash are/were stored. Avoid direct exposure of traps to lint dust. b. Note the date of installation with a marker pen and replace the pheromone septa at intervals specified by the manufacturer. Inspect the traps for moth catches weekly and destroy them.
- After the ginning season is over, clean the entire mill area, leftover kapas and bury the trashed seeds.