 ਵਾਪਸ
ਵਾਪਸ

Organic methods of cultivation plays an important role in maintaining soil health. There are many easy methods that farmers can adopt like using appropriate biofertilizers to increase soil fertility.
What are Bio fertilizers :- Living microorganisms of bacterial, fungal, and algal origin are called bio-fertilizers. Scientists have identified effective strains through research to match specific soil and climatic conditions. These strains can be produced in large quantities also in a lab and given to farmers. They can be packaged in mediums like peat or lignite powder as carriers so that they will have a long enough shelf life.
List of Commonly Produced Bio-fertilizers in India 1. Bacterial Biofertilizers: Rhizobium, Azospirilium, Azotobacter, Phosphobacteria. 2. Algal Biofertilizers: Azolla.
List of Commonly Produced Bio-fertilizers in India 1. Bacterial Biofertilizers: Rhizobium, Azospirilium, Azotobacter, Phosphobacteria. 2. Algal Biofertilizers: Azolla.
1.Bacterial Biofertilizers
1.Bacterial Biofertilizers
Rhizobium strains: Rhizobium strains can be used in crops like Legumes like pulses, groundnut, soybean. it will increase the yield up to 10-35% and fix 50-80 kg Nitrogen per acre.Azotobacter:- Azotobacter can be used in crops like non- legume crops including dry land crops. Using of azotobacter increases 10-15% yield and fix 10-15 kg N/acre. Azospirillum:- Azospirillum can be used crops like non-legumes like maize, barley, oats, sorghum, millet, Sugarcane, rice and by using this biofertilizer 10-20% yield can be increased.Phosphate Solubilizers (Phosphobacteria) Phosphobacteria:- Applied to soil for all crops which can lead to increase 5-30% yield.
Application Methods of Biofertilizers
Application Methods of Biofertilizers
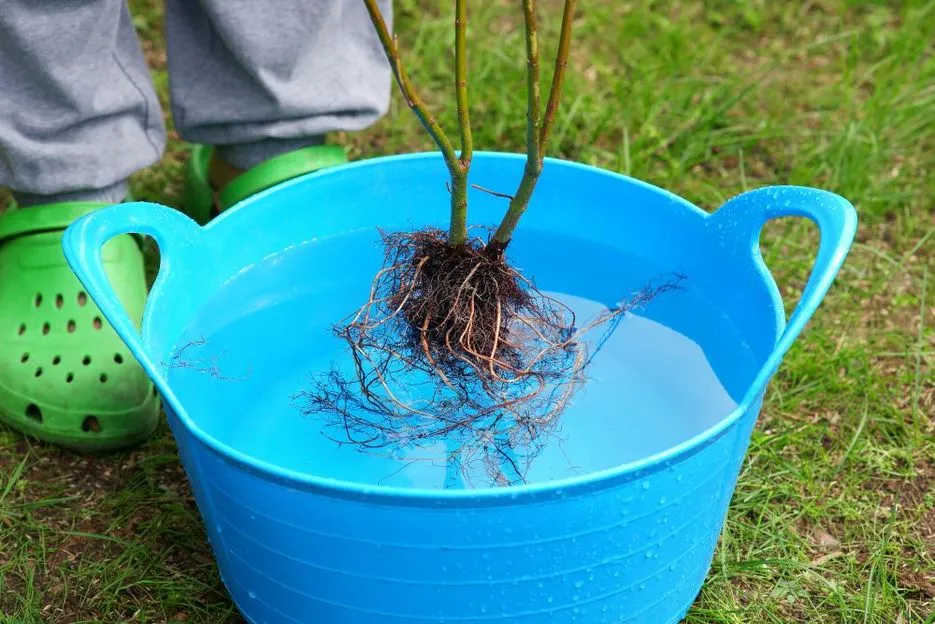
Seed Treatment of Rhizobium, Azospirillum, Azotobacter and Phosphobacteria:
Seed Treatment of Rhizobium, Azospirillum, Azotobacter and Phosphobacteria:
Each packet of inoculant (200g) is combined with 200 ml of rice gruel or jaggery solution. The seeds needed for one acre are mixed in the slurry to ensure a uniform coating of the inoculants, and they are then shade dried for 30 minutes. The treated seeds must be used within 24 hours. 10 kg of seeds can be treated with one package of inoculant.


Soil Treatment
Soil Treatment
200 kg of compost are combined with 4 kg of each of the suggested biofertilizers and the mixture is left overnight. Before sowing or planting, this mixture is incorporated into the soil.


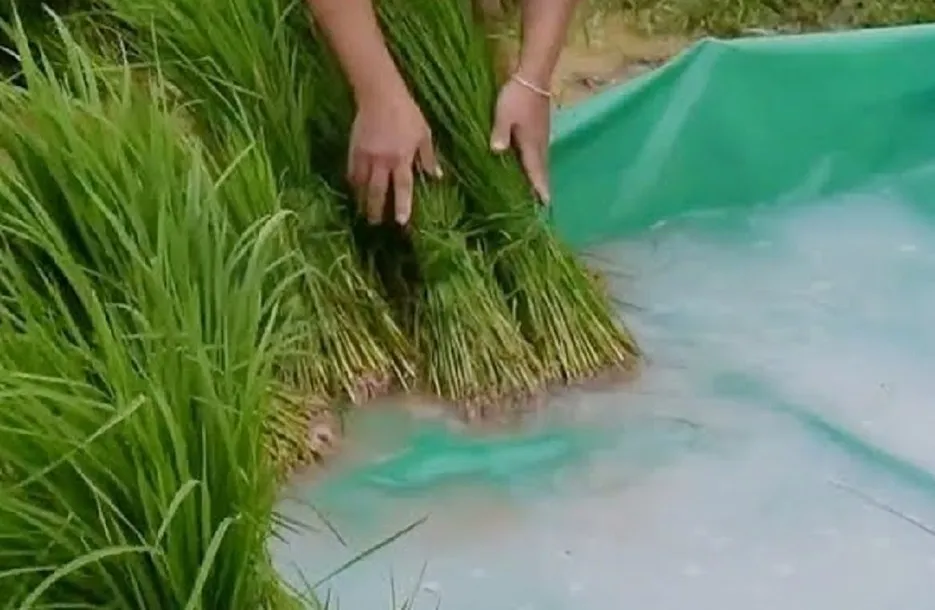
Seedling root dip
Seedling root dip
For transplanted crops, this technique can be utilised by using 40 litres of water with five packets (1.0 kg) of the inoculants for one ha of land. The seedlings are transplanted after being submerged in the solutions for 10 to 30 minutes at the root end. For seedling root dip, especially for rice, Azospirillum is used.


Precautions for the use of Biofertilizer
Precautions for the use of Biofertilizer
• Biofertilizer should be stored in cool and dry place (25-40 degree Celsius). Avoid direct contact with sunlight.
• It should be specified to specific crop with recommendation doses.
• While purchasing a packet of biofertilizers ensure about of name of the crop for which intended, date of expire date of manufacture and formulation name.
• Biofertilizers should be used as a supplement to the chemical and organic fertilizers.
Preparation of strains: (Example: Rhizobium strains)
Preparation of strains: (Example: Rhizobium strains)
Collect soil from healthy plant rhizosphere and dry it followed by grinding and through serial dilution prepare the rhizobium sample. Place the sterilized media (manitol agar media) on the sterilized petri plate and cool it. Add few drops of sample and incubate it at 45 degrees Celsius and after solidification rotate the petri dish and get the culture with 4-5 days. Same culture can be added to charcoal (base material) and marketed or applied into farm fields.
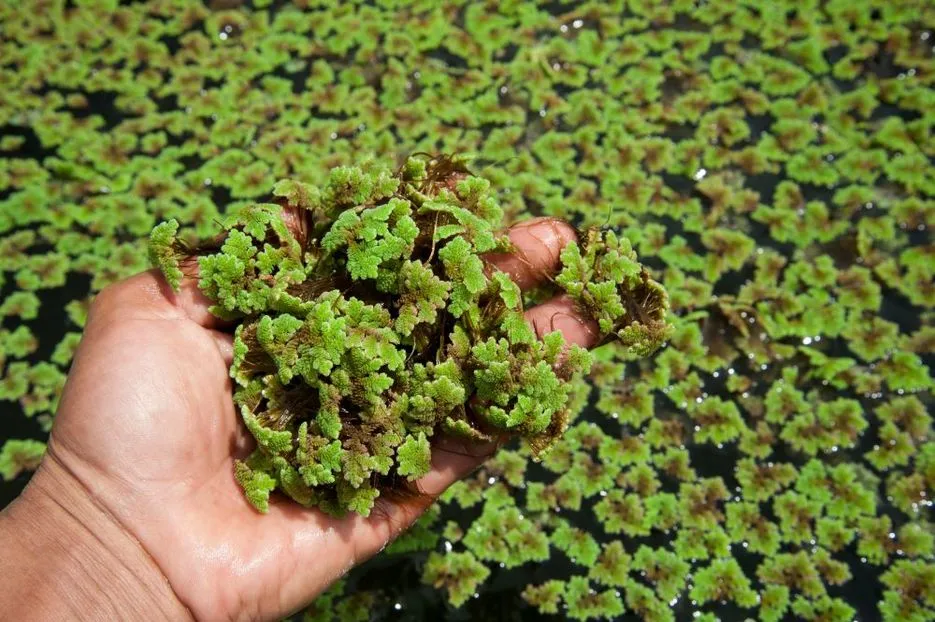
Azolla It is suited in Rice/wetlands crops, Azolla can give biomass up to 40-50 tonnes and fix 15-40 kg N/acre.
Cultivation process of Azolla:
Cultivation process of Azolla:
1.Prepare a tank size of 2m X 1m X 15 cm with bricks on the bund and spread polythene sheet over the tank
-
Add 25 kg of clean soil into the tank and apply it to uniformly across the pond and 10 kg Rock phosphate per acre
-
Mix 5 kg of cow dung into the tank.
-
Maintain water depth of 15 cm in the tank.
-
Apply 500g of azolla culture per m2 into the pond.
-
Apply carbofuran 3g granules @ 2-4g per m2 to reduce the pest attack like hairy caterpillar.
-
After 1-2 weeks azolla will fully cover the pond and it is ready to harvest. 8. Everyday 1-2 kg of azolla can be harvest.
Maintenance of azolla tank
Maintenance of azolla tank
1.Apply 2 kg of cow dung in every 2 weeks intervals
-
Remove ¼ of water from tank and refill with fresh water once in 2 weeks
-
Remove the old base soil and add fresh soil into the tank
-
Tank need to empty once in every 6 months and cultivation need to be restarted with new culture.
-
Maintain temperature of 25-35 degree Celsius and pH between 5.5 to 7
Use of Azolla:
Use of Azolla:
-
Azolla is planted one to three days after rice is transplanted, at a rate of 100 g/m2 (500 kg/acre) and left to multiply for 25 to 30 days. After first weeding, azolla fronds can be integrated into the soil.
-
Azolla can be added to the animal’s regular diet in the amount of 2-2.5 kg of azolla per animal or can be given with the other feeds with 1:1 ratio.


Availability of biofertilizers for farmers:
Availability of biofertilizers for farmers:
All types of biofertilizers are available at nearest Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs). Nowadays all the biofertilizers available in online sites also.
Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!