 மீண்டும்
மீண்டும்

Mentha is also known as a cash crop in the agricultural sector, although it has been used for various medicines in Ayurveda for decades, hence the cultivation of mentha (mint) is in many areas of India including Kashmir, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand. Currently, Mentha is grown in Uttar Pradesh in large areas, but cultivation is getting popular in many areas because of high demand. Due to the high demand for mentha, many companies provide seeds, fertilizers, and other facilities for its cultivation, and also buy products at a higher price. Demand for mentha oil has been steadily increasing due to its use from medicine to cosmetics and food items, due to which farmers are getting very good profits, and India is its largest producer. Various government and non-governmental institutes also organize periodic work for the cultivation of mentha from time to time and various schemes have been made by the government for the cultivation of mentha which farmers can cultivate by obtaining grants.
Types of Mentha
Types of Mentha
Different varieties of mentha are cultivated in different regions based on geographical and environmental conditions, such as aquatic mentha, buddhia mentha, Japanese mint, and black mint. The most preferred species being Japanese mint, cultivated in Uttar Pradesh. In Bihar and some parts of Madhya Pradesh, it is grown in abundance. This variety can be cultivated even in moist swampy areas, grasslands in which the drainage system is not suitable, in such a situation, it has a height of up to 1 meter, The leaves are oval in shape and slightly red or green in color, Generally, the farmer gets 200 - 220 kg yield and 80-85 kg mentha oil in one are field.


Climate
Climate
Mentha can be cultivated in all types of environments, is considered suitable for its cultivation.


Land
Land
Light loam, slightly sandy soils having drainage system, organic soils having Ph 6 to 7 are suitable for a good yield, deep plowing before plouging, and two Run the bar and the slant plow, which should be soaked and spread properly in the soil of the plant.


Manures and Fertilizers
Manures and Fertilizers
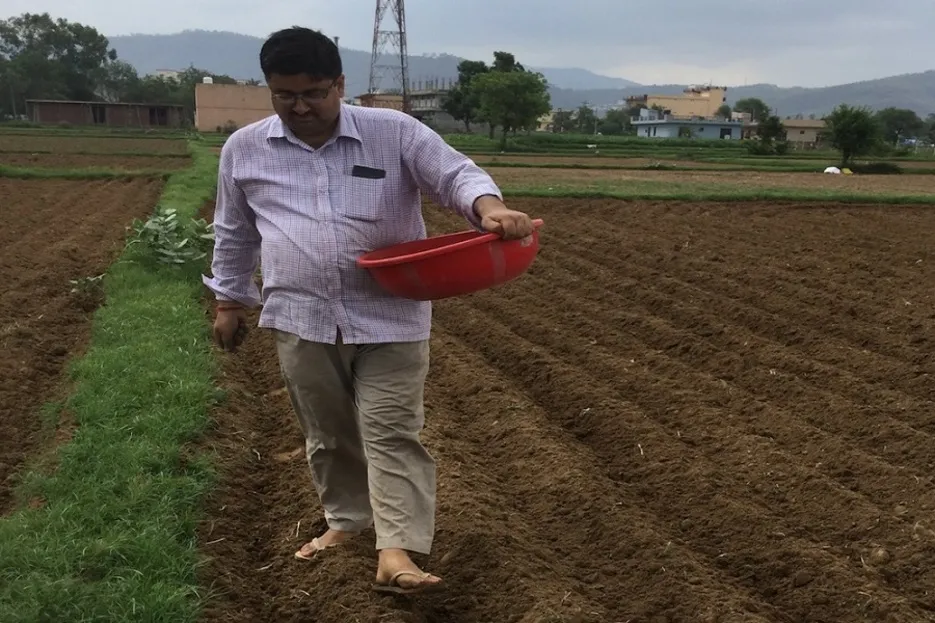
Make sure to check the soil before use of fertilizer, and use 100 kg of Farmyard manure and 150 kg NPK / acre in the soil while running the plow. Zinc deficiency is common in many areas. Therefore 20 kg Zinc sulfate should be mixed in the soil at the time of land preparation.


Transplanting
Transplanting
From the end of February to March time is suitable for transplanting of mentha, seeds and Sakara (tano) are used for transplanting, they should be treated with Trichoderma before sowing if directly sown. If it is, keep it 4 to 4 cm apart from row to row and keep the depth of the pit not more than 3 cm, then lightly irrigate after transplanting.


Weed control
Weed control
For mentha cultivation, before sowing, farmers have to remove weeds by machine or hand, and after 30 days spray recommended weedicide. as mentha crop is very dense, so inspect the crop from time to time and make a decision on a real-time basis, you can spray weedicide or remove it by the manual pick.


Intercropping
Intercropping
Mentha can also be cultivated with other crops, which may benefit the farmer more, Mentha is cultivated in abundance with a vetiver crop as the maturation of both crops takes 90 - 120 days. And fertilizer requirements are also same. Apart from this, mentha is also cultivated with garlic crop, garlic is sown in November and after two months mentha can be planted in the remaining area of the field, which will give double benefit to the farmer, along with it. farmers can take mentha crop along with sugarcane.


Disease and Control
Disease and Control
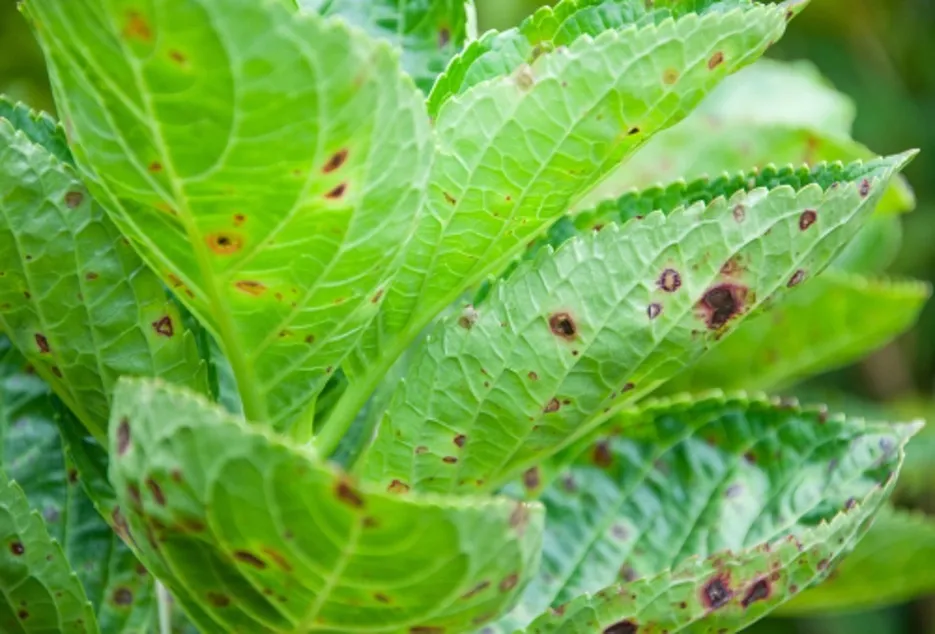
Leaf spotted disease
Leaf spotted disease
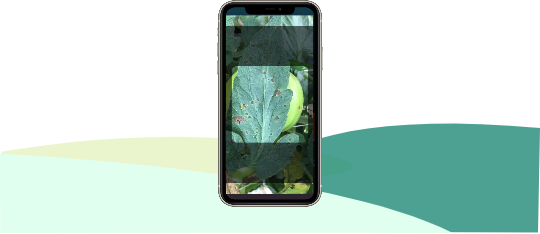
It is a fungal disease, the symptoms of which appear in the back and visible spots of the leaf, which leaves the leaf fall yellow, for the prevention of copper oxychloride, dithane as directed by 20 K. Spray in intervals


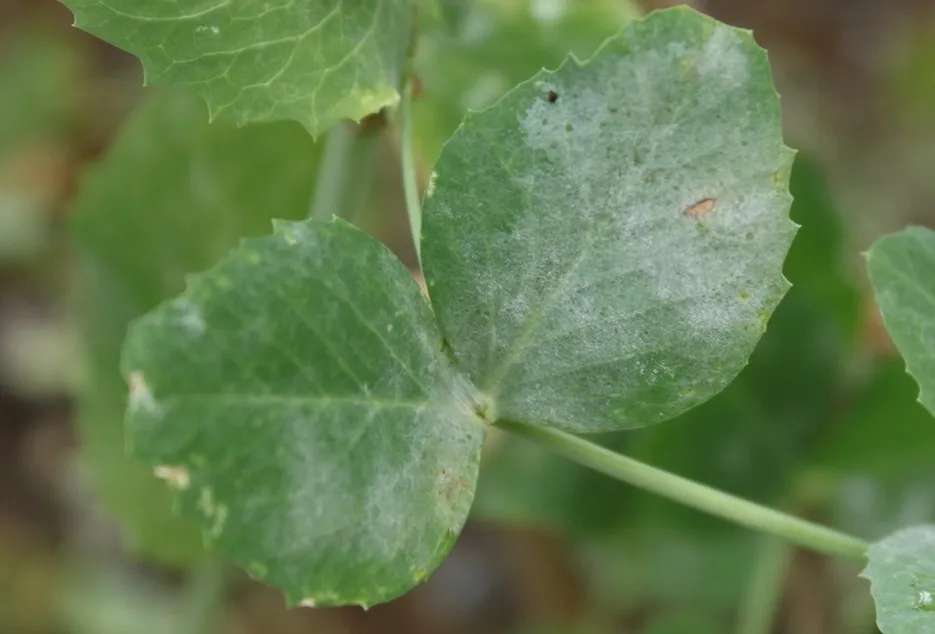
Powdery Mildew
Powdery Mildew
It is a fungal disease, in which white spots appear on the plant, the plant weakens and dies, for which proper fungicide should be used for prevention.


Insect damage and control
Insect damage and control
Hairy caterpillar
Hairy caterpillar
The effect of Sundi is more in cold areas, yellowish-brown up to 3 cm length larva can be seen on the plant which eats the green leaves of the plant which has an effect on the yield, for which prevention Use appropriate pesticides after consulting agricultural experts.


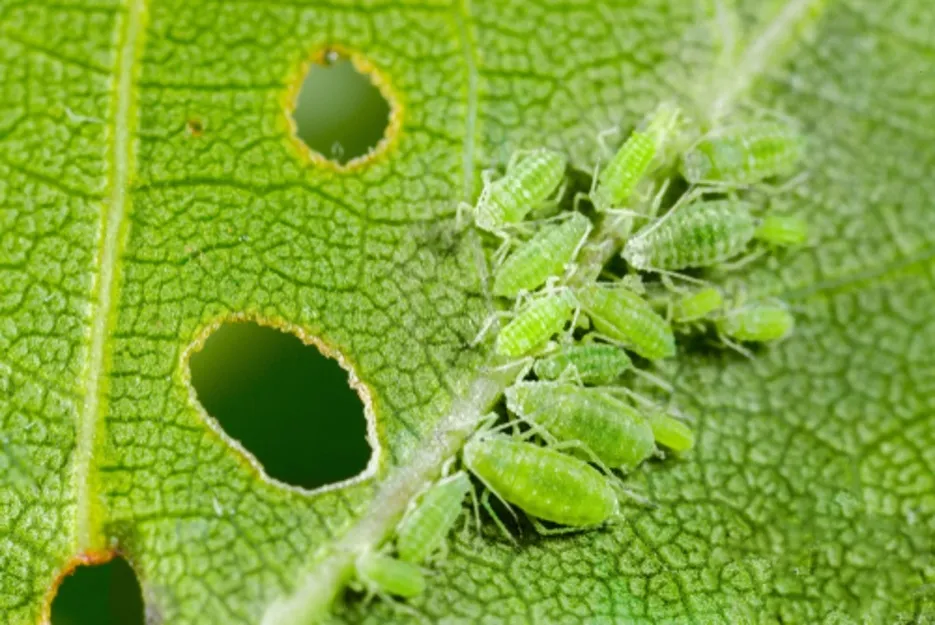
Aphid
Aphid
This pest attacks infant plants and sucks sap from the plant. The outbreak of this insect is more in the month of April- Jun which stops the growth of plants, to control the damage, use effects of foliar application.


Harvesting
Harvesting
Mentha crop is ready for harvesting in 100 to 120 days, crop can be harvested 2 to 3 times depending on the season and type, the amount of oil in the leaves when the crop is not harvested at the right time. Decreases, so do the first cut immediately after flowering


Benefits
Benefits
By selling mentha leaves directly in the market, farmers can earn profits, but more profits can be obtained by selling mentha oil. usually 80 to 85 liters of mentha oil from one acer . Can be obtained, whose market price can be obtained from 1200 to 4000 rupees per liter, as well as many beauty producers and pharmaceutical companies buy it directly from farmers at reasonable prices.


Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!