 மீண்டும்
மீண்டும்
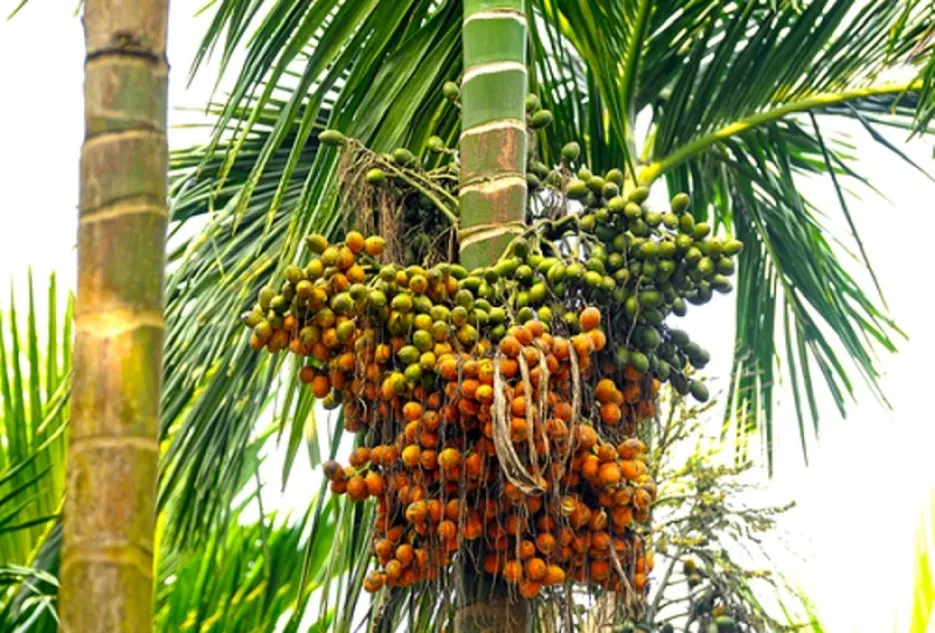

Many farmers in Karnataka and Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and other states are planning to plant Arecanut plantations due to good profits and returns. Are you interested in growing the Arecanut crop? Please find important suggestions below.
Soil & Climate condition required
Soil & Climate condition required

Areca nut grows well in less fluctuating temperatures within the range of 15°C and 35°C and is adversely affected by temperatures below 10°C and above 40°C. Areca nut is very sensitive to high temperature and water stagnation.


Varieties for cultivation
Varieties for cultivation
There are few recognized promising local verities that adapt well to the local environmental conditions and are generally tall growing in nature and takes about 6 years forbearing. They are Thirthahalli Local, South Kenra Local, Shriwardhan and Hirehalli.There are few Improved verities that are developed by various universities and these improved verities come for bearing early and produce homogeneous sized nuts and have better yielding capacity.
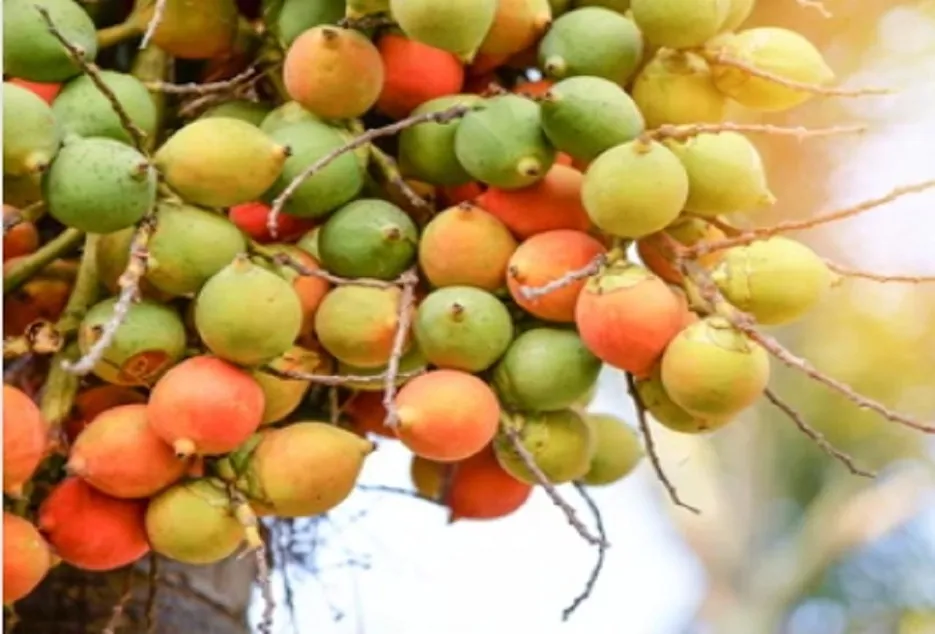
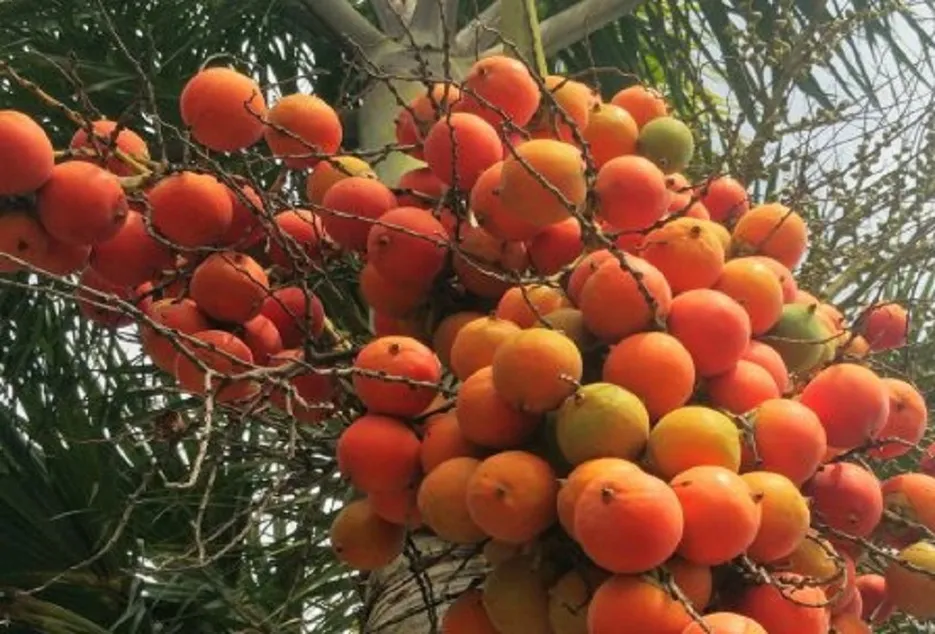


Varieties suitable for
Varieties suitable for
Coastal Climate : Mangala, Sumangala, Sreemangala, Sarwamangala, Vittal Areca Hybrid1 & 2 West Bengal: Mohit Nagar Assam and North east : Kahikuchi (VTL-64) Andaman & Nicobar : Calicut-17
Raising of Seedlings
Raising of Seedlings
Areca nut can be propagated only from seeds and below are the steps to be followed
Selection of mother palm
Selection of mother palm
Early bearing, regular bearing, growing more number of leaves, shorter internodes and high fruit set are the ideal characters of mother palm and it should be free from pest and diseases and should be of middle age.
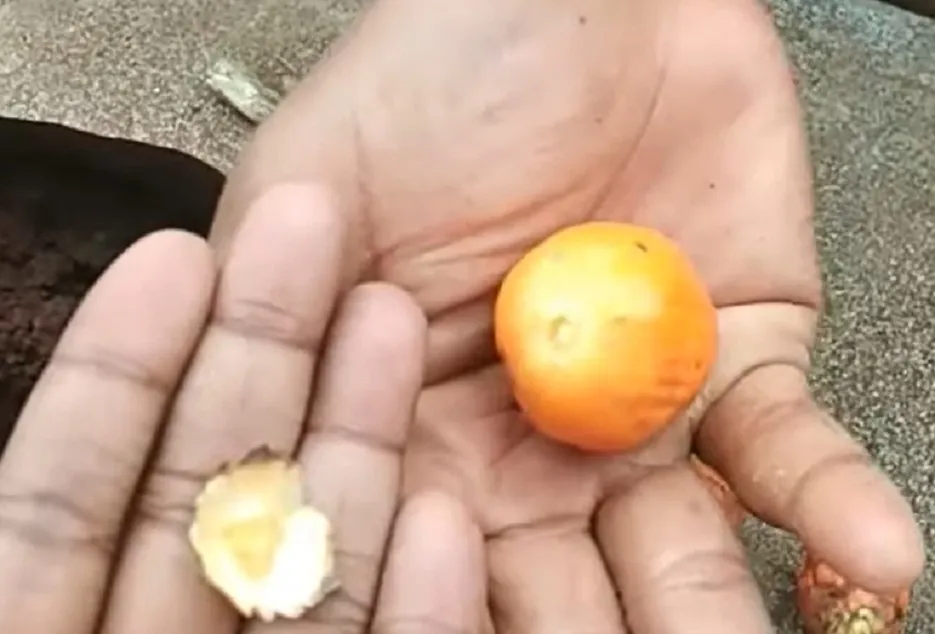
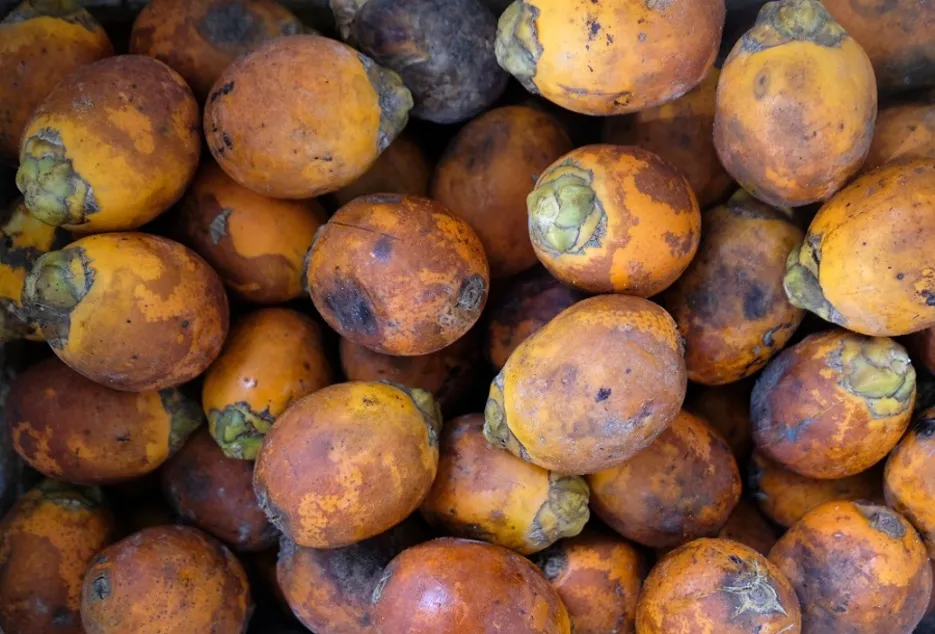


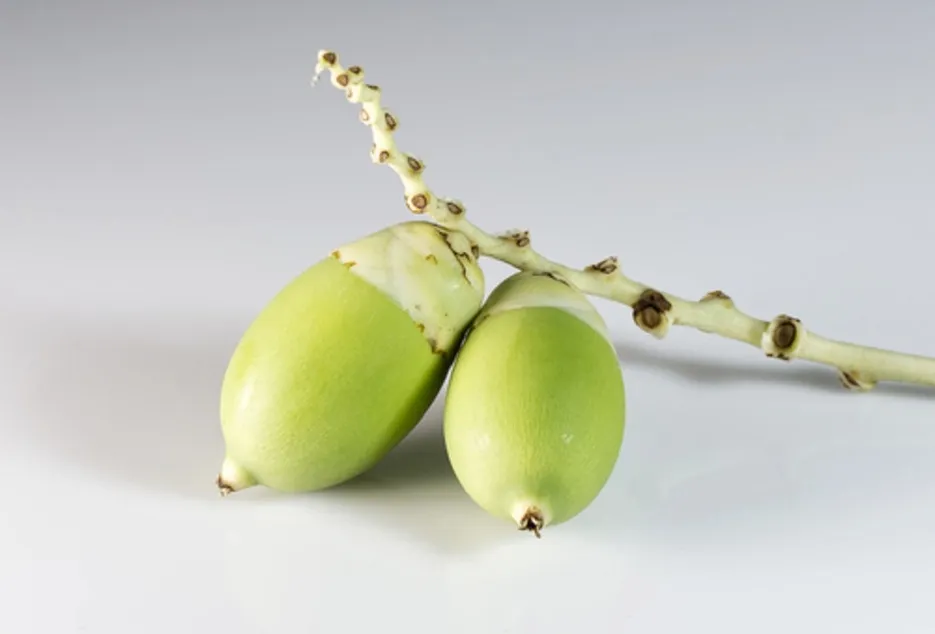
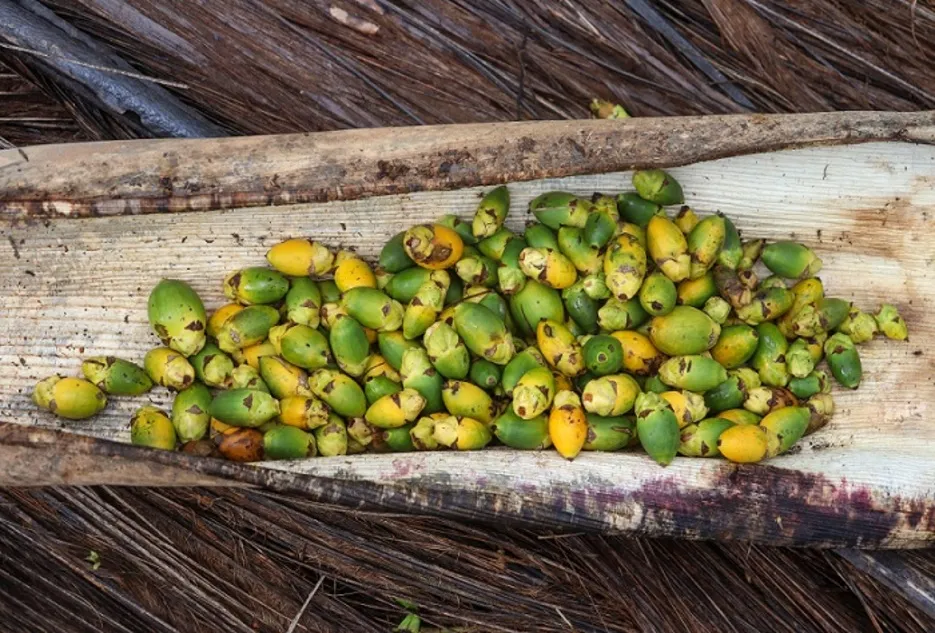
Selection of seed nut
Selection of seed nut
Fully ripened nut with above 35 grams should be selected, nuts should be selected from the middle bunch of the tree during 2nd or 3rd harvest of that year. The selected nuts should float vertically with calyx-end pointing upwards when allowed to float on water. These types of nuts produce the seedlings of faster and healthy growth.


Nursery management
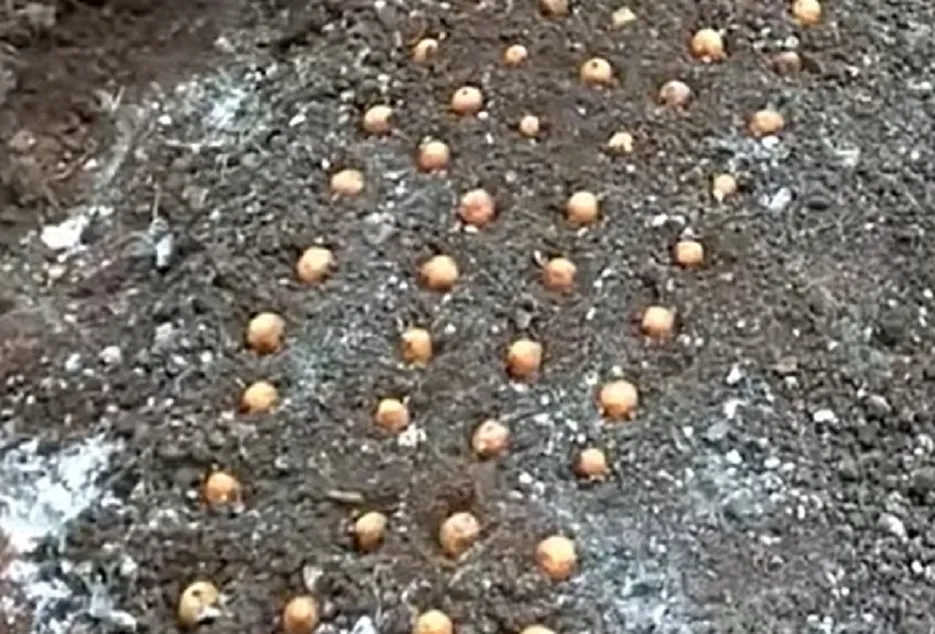
Nursery management
Selected whole nut should be sown immediately after harvesting into the nursery bed with 10 cm spacing between nuts and should be watered daily. Nuts should be vertically sown with Calyx-end (stalk-end) facing upwards and a thin layer of sand is covered over it and the nursery bed should be mulched with paddy straw or areca leaf. After 3 months seedling should be transplanted into a secondary nursery bed with 30 X 30 cm spacing or can be directly transplanted in to 150-gauge Polythene bags of size 25 X 15 cm filled with a mixture of Topsoil: FYM: Sand in the ratio of 7:3:2. Seedlings should be always kept in shade and irrigated regularly.




Selection of seedlings
Selection of seedlings
Seedlings raised in polybags, establishes well in the main field, 12 to 16 months old seedling with 5 or more leaves with “less height” and “more collar girth” should be selected for planting.


Spacing
Spacing
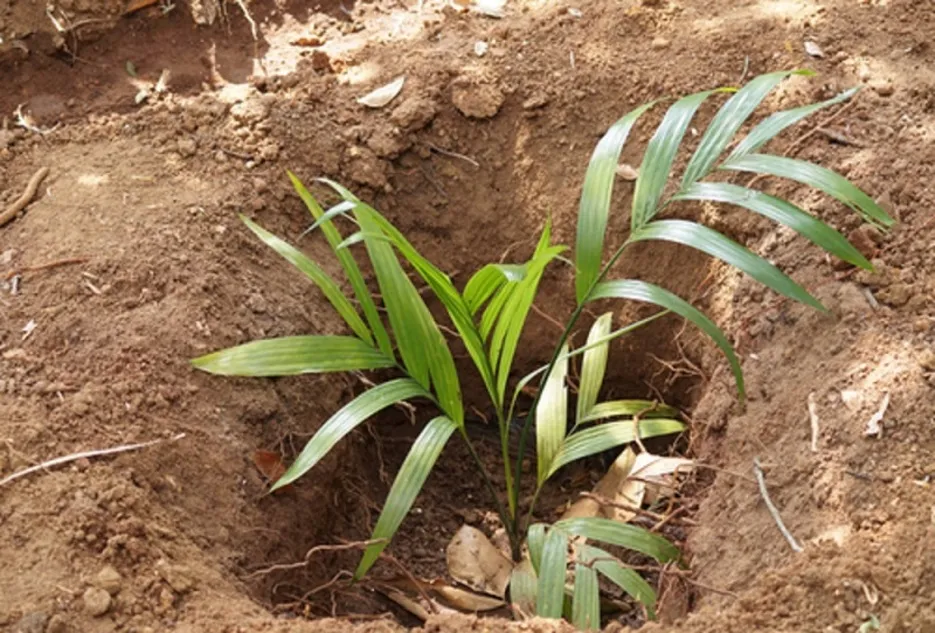
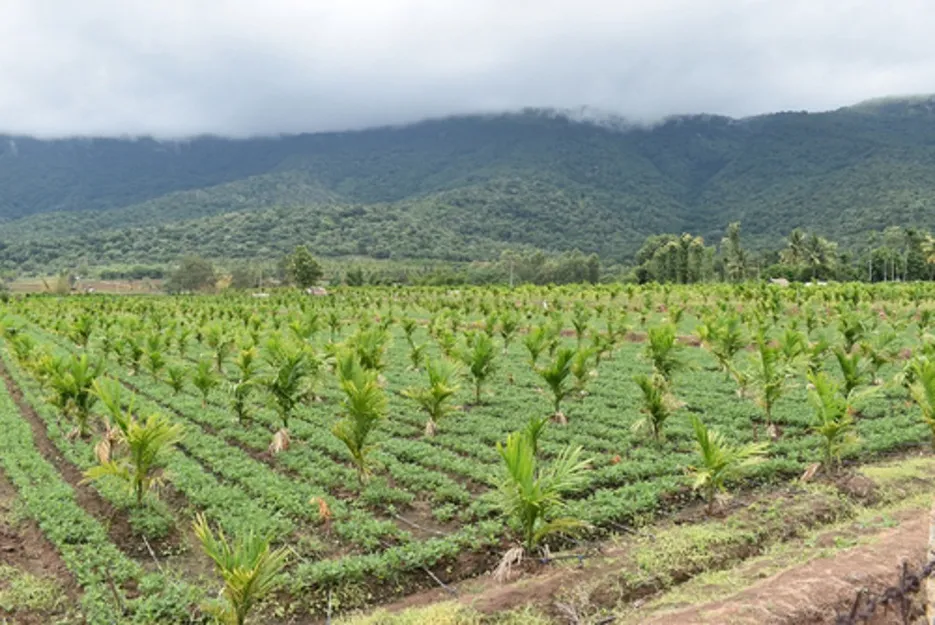
Generally, 9 feet x 9 feet is followed with this almost 538 plants can be planted per acre, apart from this, 10 feet between row and 8 to 10 feet between plant can also be followed, this wider row spacing is followed for talking up of intercropping.


Season of Planting
Season of Planting


Planting is generally done during May – June, as the onset of monsoon rain. And in areas with very severe monsoon rains like in western coastal areas and in areas with poor water drainage, planting should be done in September - October month and seedling should be regularly irrigated until the rain starts.
Shading
Shading
Areca nut seedlings are highly susceptible to sun scorching, so areca leaf sheath or leaf should be used with the help of wooden pegs to support to block the direct sunlight which comes during the afternoon to evening time (12 pm to 4 pm) from the south and south-west direction. Only the sunlight falling area should be covered and remain side should be kept open for airflow. Shade can also be provided by growing banana crops between the rows of areca nut seedlings.
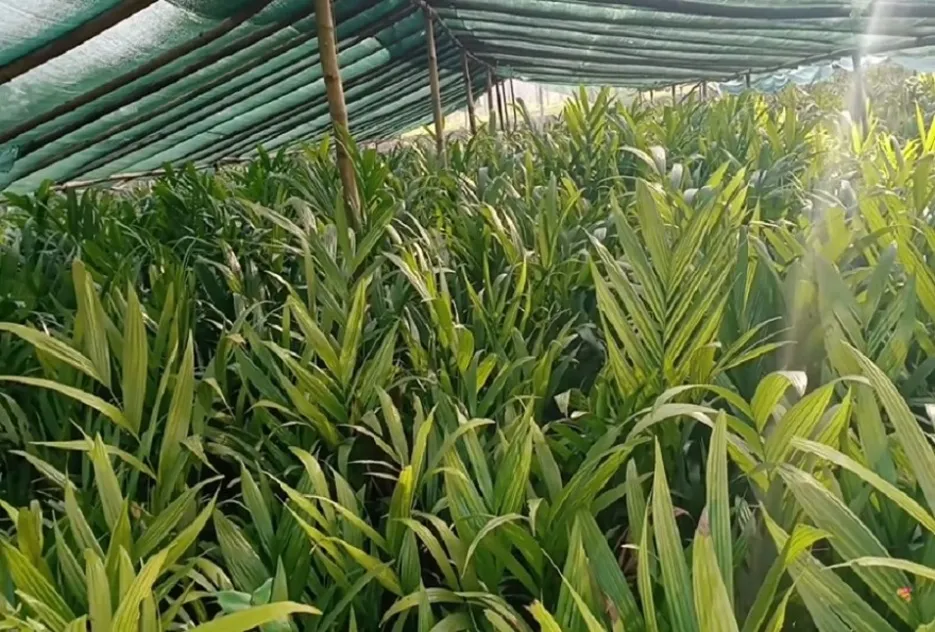
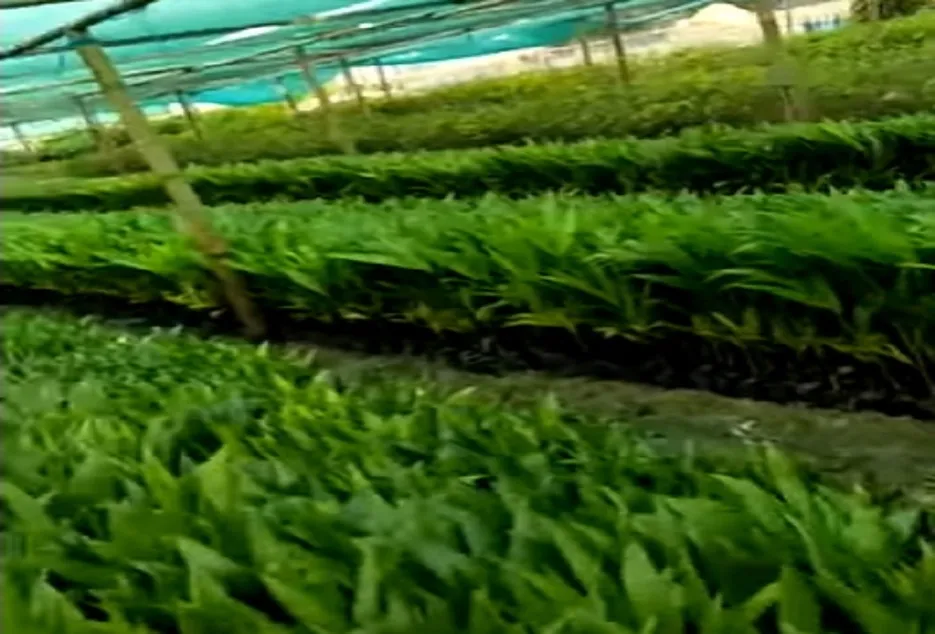


Nutrient Requirement and Management
Nutrient Requirement and Management
Areca nut requires the application of nutrients in split doses throughout the year as it is a perineal crop. 100 g N (220 g rea), 40 g P (200 g rock phosphate) and 140 g K (235 g muriate of potash) should be given in 3 or at least 2 split doses along with 12kg of green manure and cow dung manure per tree per year.
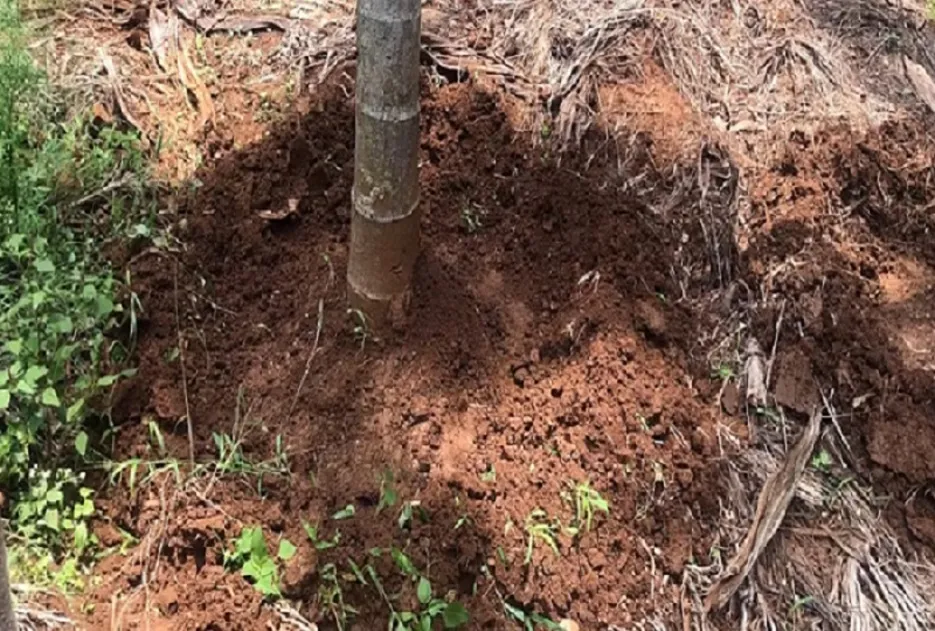
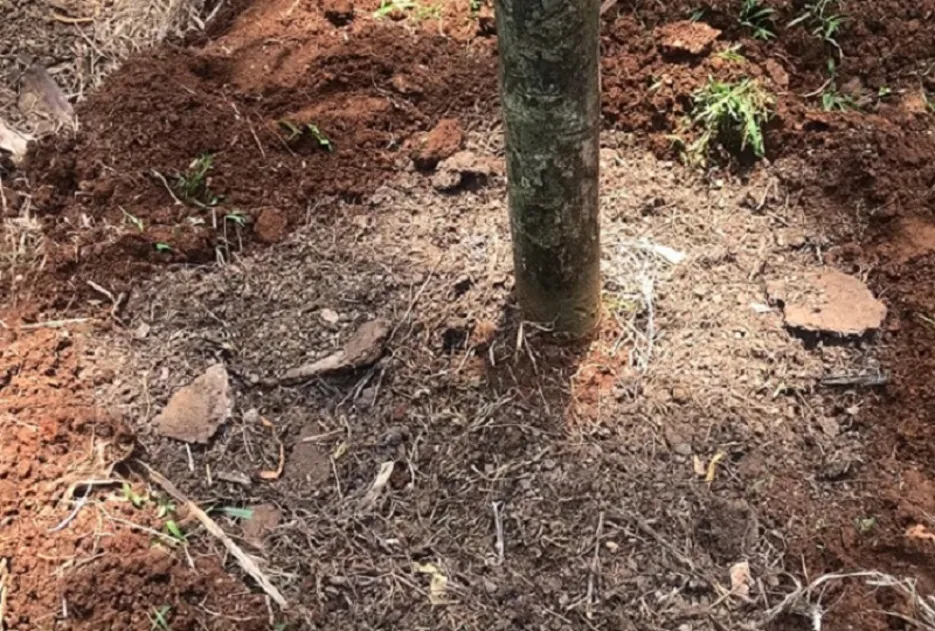


Inter-Cultural Operations
Inter-Cultural Operations
After monsoon rains are over in the month of October – November, weeding should be done and light digging / ploughing is done to break the hard soil crust, once in 2 years based on the soil pH Lime or Gypsum is added during this light ploughing to maintain the soil at neutral pH.


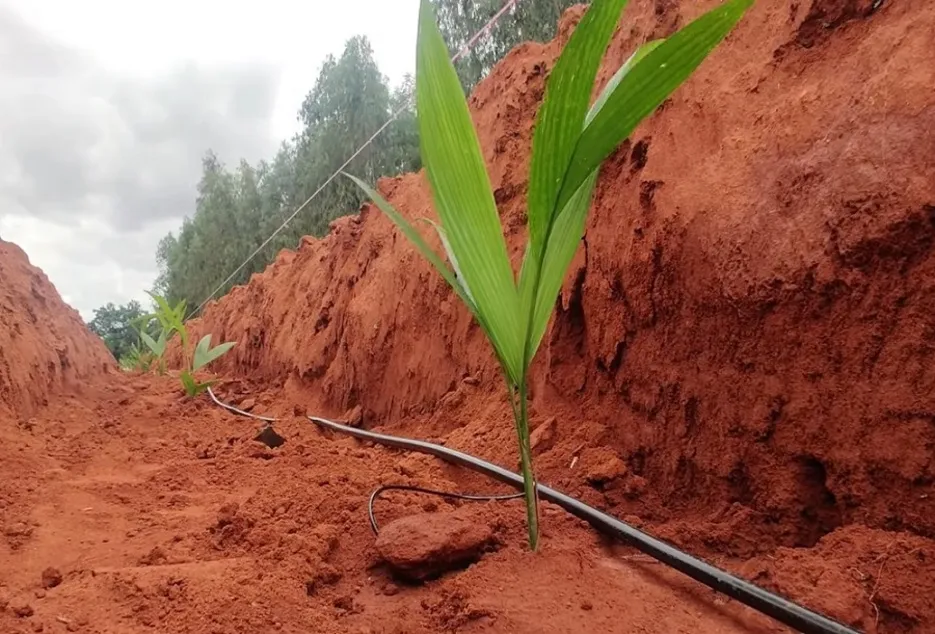
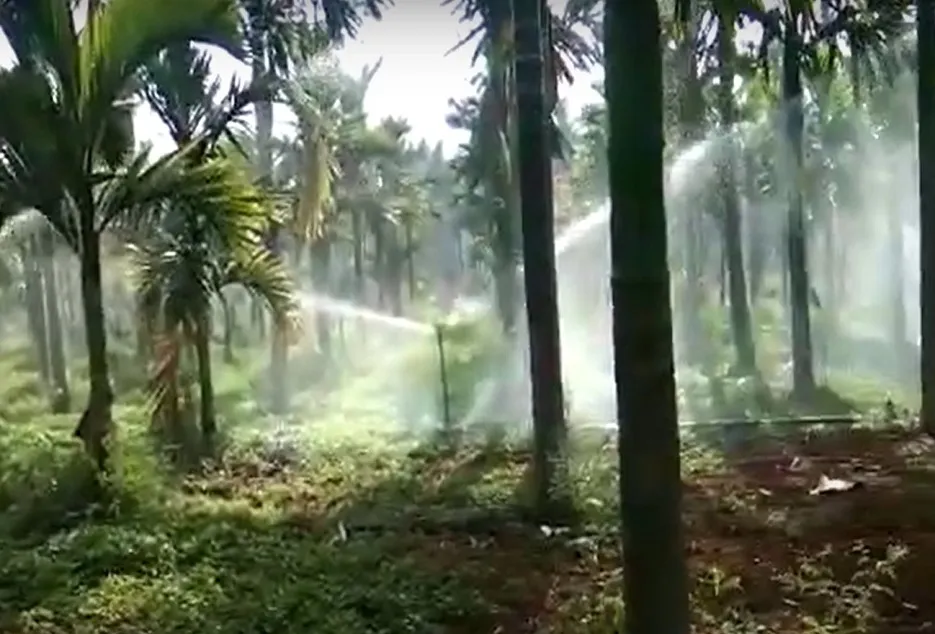
Irrigation
Irrigation
The sprinkler irrigation system is good if intercrop is grown along with areca nut and if there is an adequate source of water. Drip irrigation should be used if water shortage is faced especially during the summer season, drip uses 1/10th of water used in sprinklers. With the drip system installed, recommended NPK and micronutrient fertilizers can be given along with water by splitting the recommended dosage into 10 parts and should be applied once in 20 days from November to May to get better results.


Intercropping / Mixed cropping
Intercropping / Mixed cropping
During the initial 5 years after planting, intercropping of Banana is done as it also provides good shade for seedings, other than this intercropping of vegetables, flower crops, medicinal plants & Legumes can be done during the initial 5 years. Growing Intercrop controls weeds and can be used as green manure and mulching. Legumes also help in soil nitrogen fixation. 5 years after planting areca nut trees, crops like Black pepper, Betel vine and Vanilla can be grown as a mixed crops with the support of the areca nut tree by planting at the base of the tree. Based on climatic conditions crops like Banana, Lemon, Orange, Cocoa, Cardamom, Coffee can be grown by planting one plant in the space between 4 areca nut trees. On the borders of the orchard, timber trees, perineal fruit trees, spice trees and coconut can be grown.
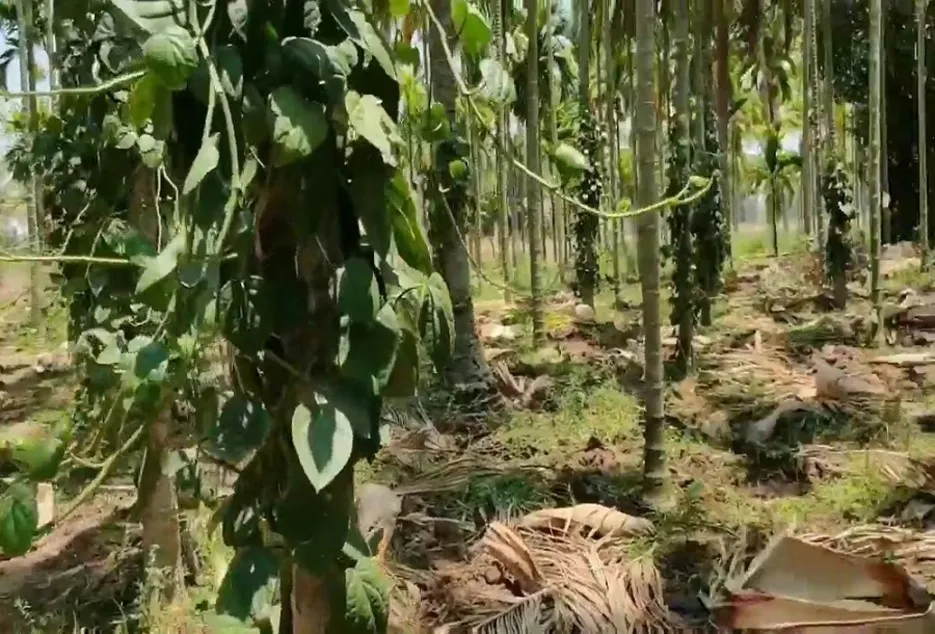


Harvesting
Harvesting
The first inflorescence which comes before 3 years after planting should be removed, to let plant have good vegetative growth. Harvesting can be done with long poles in the initial years, but to harvest from fully grown trees skilled climbers are needed who can harvest from 100 trees per day. Areca nut trees give economical yield from 7th year and up to 40th year in well maintained orchards, after 40 years the yield decrease and not economical considering the maintenance cost. When the tree becomes old a new seedling should be planted next to the old tree and once the new plant starts yielding the old uneconomical tree should be cut down.
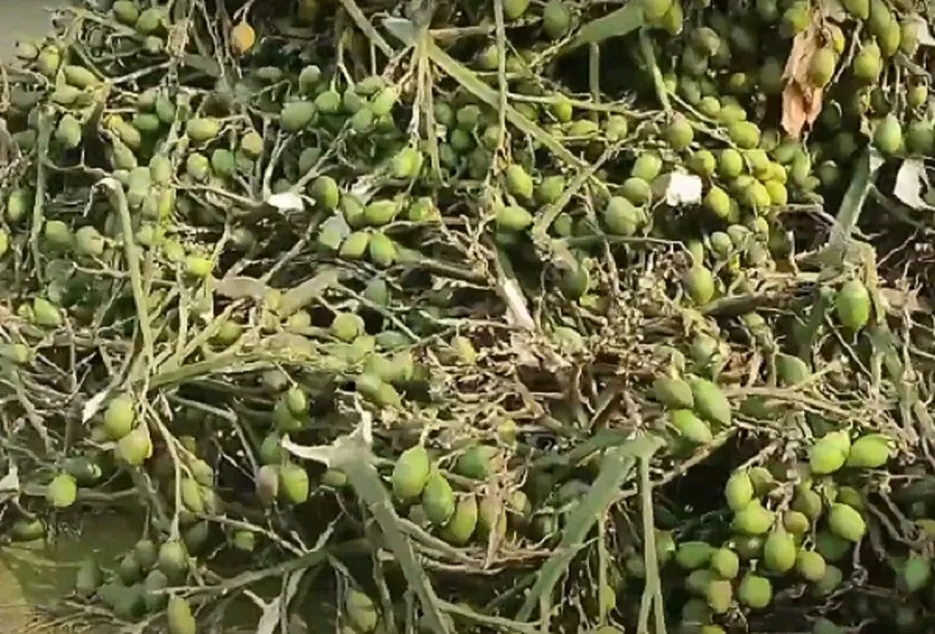
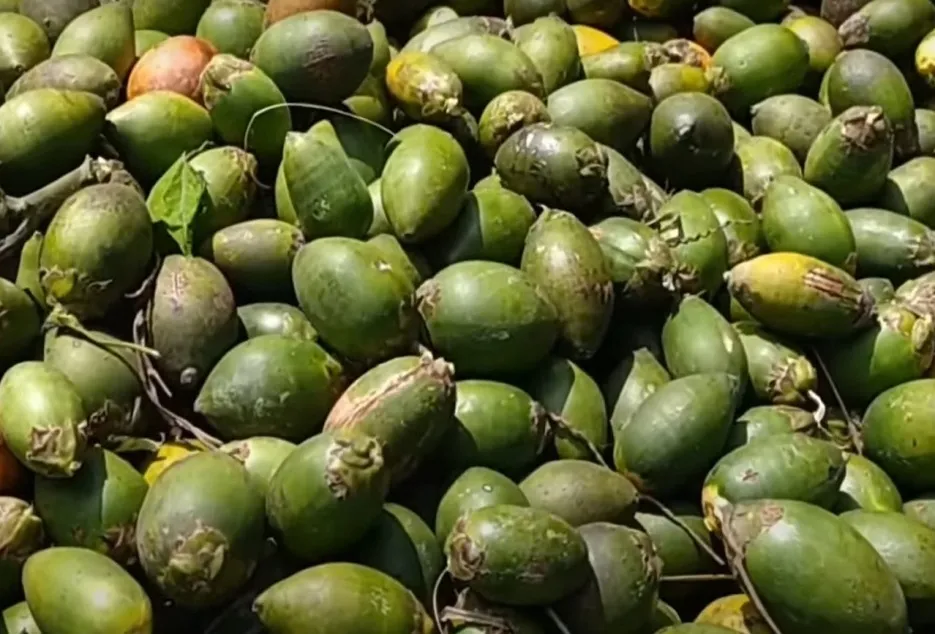


Processing & Yield
Processing & Yield
Yield depends on nutrient management and controlling of pests and diseases in the orchard. And yield quantity also varies based on the harvesting stage of the nut and mainly on type of processing done. Below are the 2 main processing types, of the areca nut.
1 Kalipak:- This type of processing is done in Karnataka and Kerala. Harvested tender green nuts are de-husked soon after harvesting, and the kernels are cut into half and these kernels are then boiled for 3 – 4 hours in “kali” or “chogaru” which is the concentrated extract obtained after boiling on 2 to 3 batches of kernels in the same water. Boiled kernels are dried well under direct sun for 5 – 7 days, and then graded and sold or can be stored until better price realization. Based on maturity level of the harvested green tender nuts, 13 to 17 kg of processed dried Kalipak can be obtained for 100 kg of raw tender areca nut. 2 Chali:- This type of processing is done in coastal parts of Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra and across Assam and West Bengal. Harvested matured ripe nuts should be well dried for 40 to 45 days under direct sun. The inner white kernel should be always white. Exposure to water or moisture due to rain or improper drying will lead to the blackening of white kernel and husk. Well-drained nuts are de-husked and then graded and sold as Chali. On average 2,000 kg of Chali can be obtained per acre.
Diseases caused in betel nut, and their prevention, we will publish in the next section. stay with us
Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!