 Back
Back
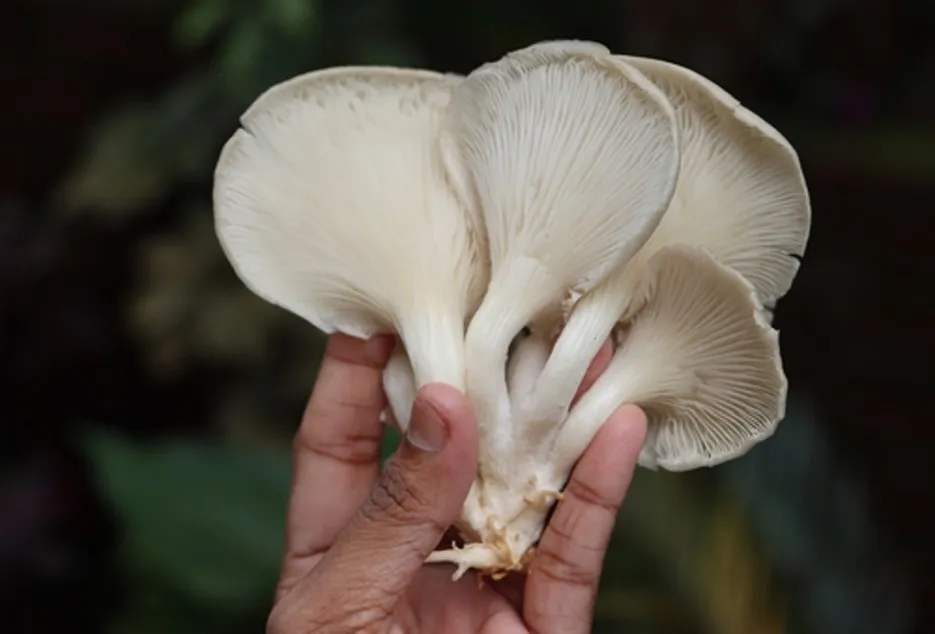

Mushroom is also known by the names of khumb,khumbi, kakutmutta etc in India . In the last few years its demand is increasing, but its production is not increasing as per the demand, Therefore, many schemes and education programs are now being run by the government and other institutions for mushroom cultivation, which farmers can take advantage of to increase their additional income, which can give big profits at low cost, recently in Uttar Pradesh. , Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra are the largest producing states of mushroom cultivation.


Suitable season and type for mushroom production: -
Suitable season and type for mushroom production: -
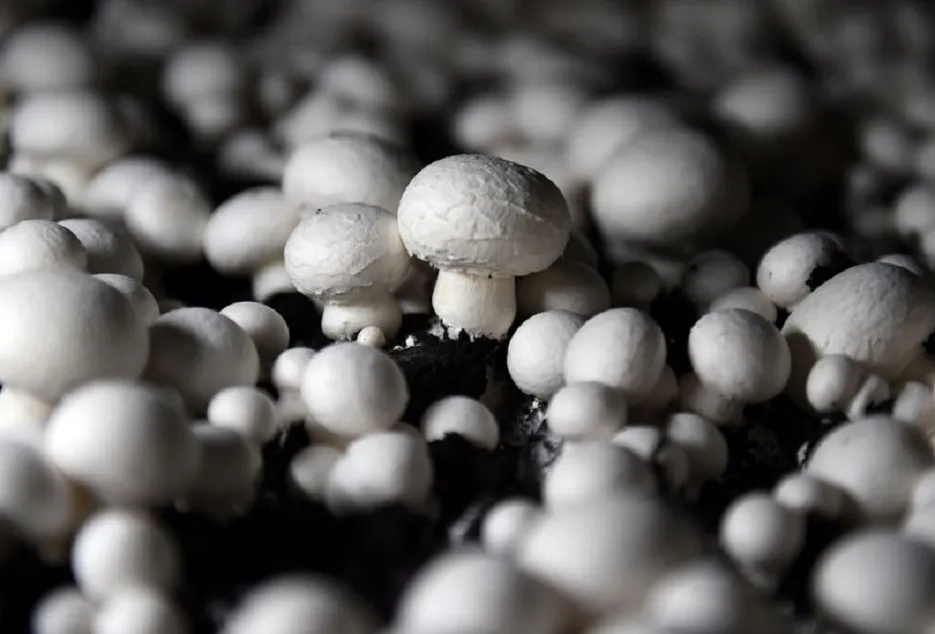
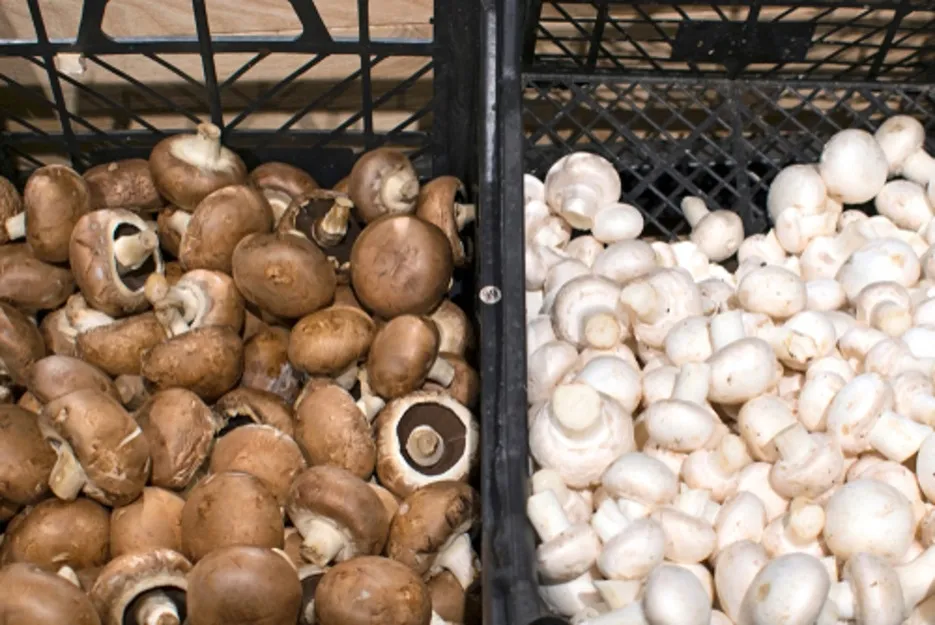
There are three most widespread varieties of mushrooms according to demand and nutritional value.1 Button mushroom2 Oyster Mushroom3 paddy straw Mushroom Oyster mushroom can be cultivated from September to November, after that button mushroom can be cultivated from February to March, and paddy straw mushroom can be grown from June to July, in this way you can grow mushroom throughout the year. Farming can earn profit, and farmers can do this farming with their traditional farming.
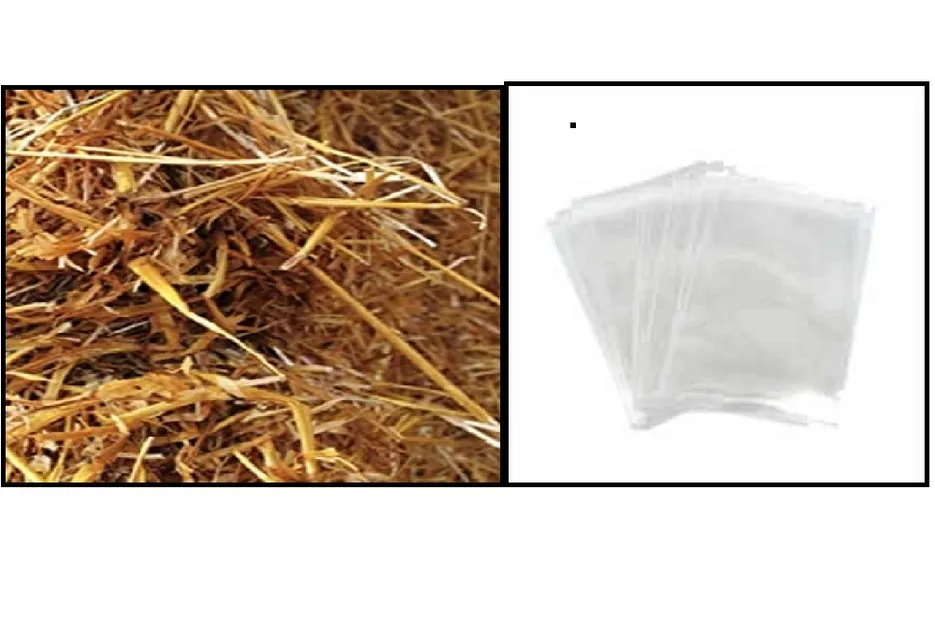
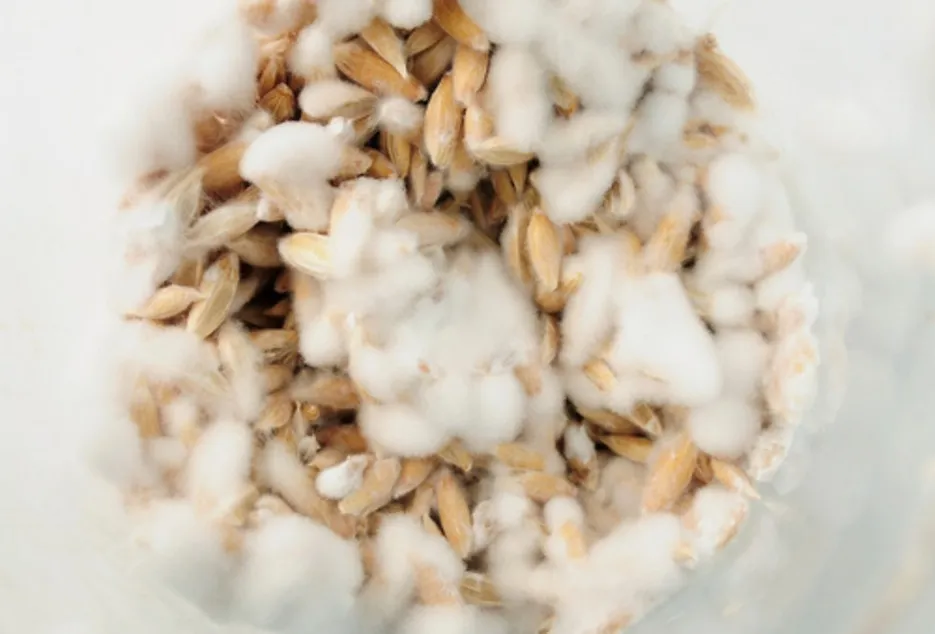
All types of climate are suitable for mushroom cultivation, and it can be cultivated from small rooms to large spaces, the most important thing for mushroom cultivation is seeds, also called spawn, spawn first Essential components are, Wheat seeds are used the most to prepare the spawn, keep this in mind and use good quality wheat, otherwise the quality of the mushroom may be bad, for starting the spawn should be done by any government Or can be bought from an agricultural institution, the cost of which ranges from 30 to 50 rupees per kg. After this the second essential item is the plastic bag there are 15 * 16, which costs 1200 to 1500 rupees per 100 bags, after that the essential component is culture, culture is the thing in which mushroom is grown for which wheat, rice, rye, cotton straw etc. is used.


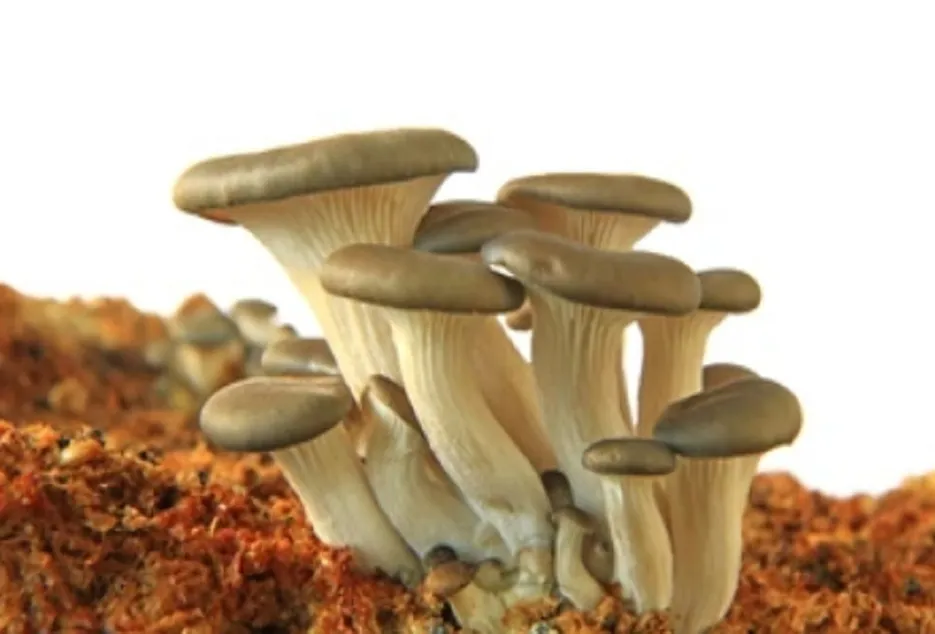
Oyster Mushroom:-
Oyster Mushroom:-
Oyster Mushroom by which farmers can increase their income by using these agricultural residues and can increase the fertility of their fields by using these agricultural residues in a scientific way. It is happening in abundance in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Orissa, West Bengal and North Eastern states. There are some characteristics of Oyster mushroom due to which its cultivation is becoming popular not only in India but also all over the world. Oyster Mushroom can be easily grown on any type of agricultural residues, its crop cycle is also 45-60 days and it can be dried easily.
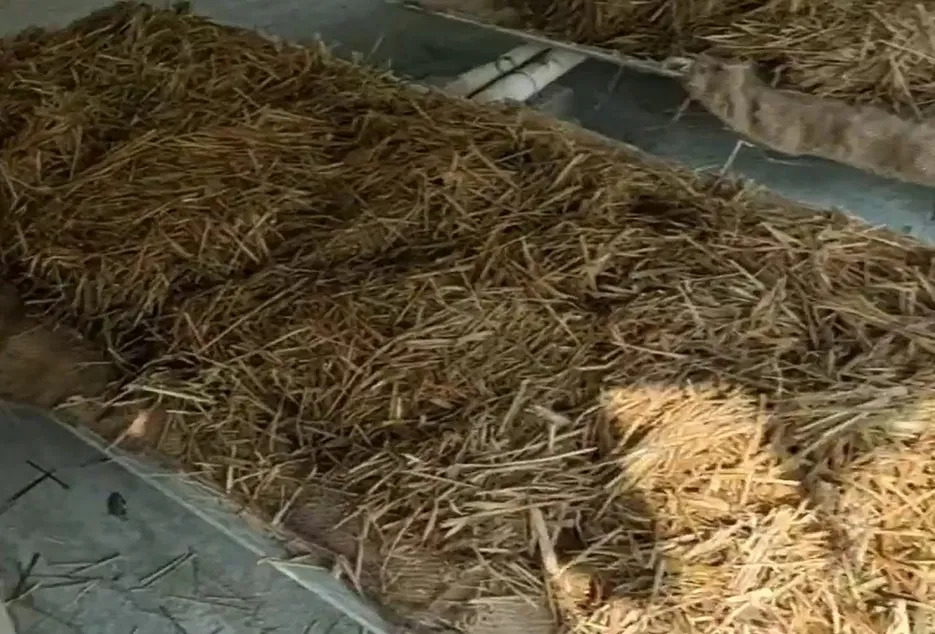
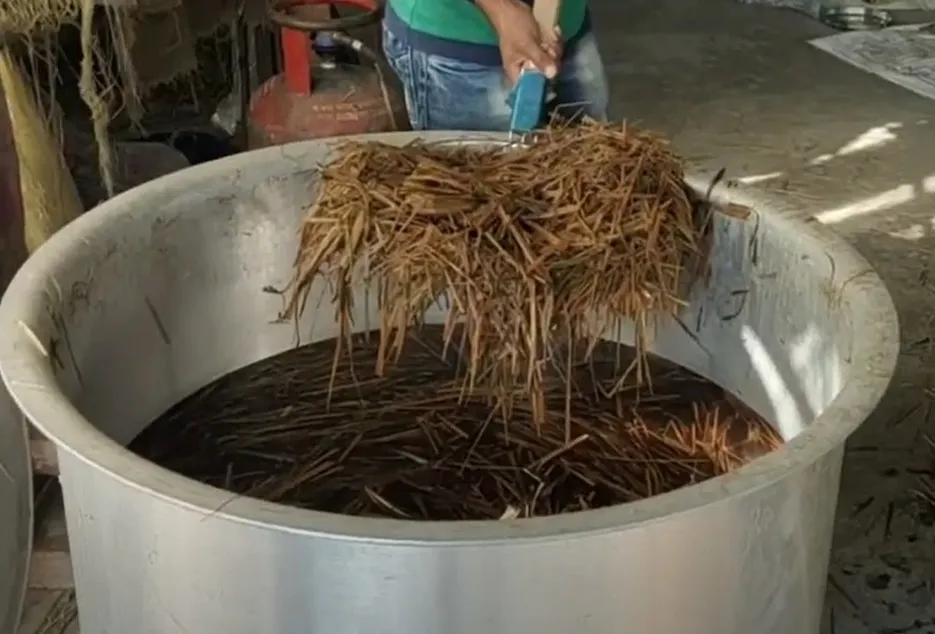
Treating the straw: -
Treating the straw: -
For mushroom cultivation, it is very important to treat the straw, the straw used should not contain any kind of bacteria, micro organisms, some methods of treating the straw are quite popular, in which all To treat with normal hot water, heat water in a large pot or drum (50 - 60 C) and boil it in water for 20 to 30 minutes, spread it on a clean foil or iron mesh and add spawn after cooling Well, this is the cheapest and easiest method of all.


Chemical method: -
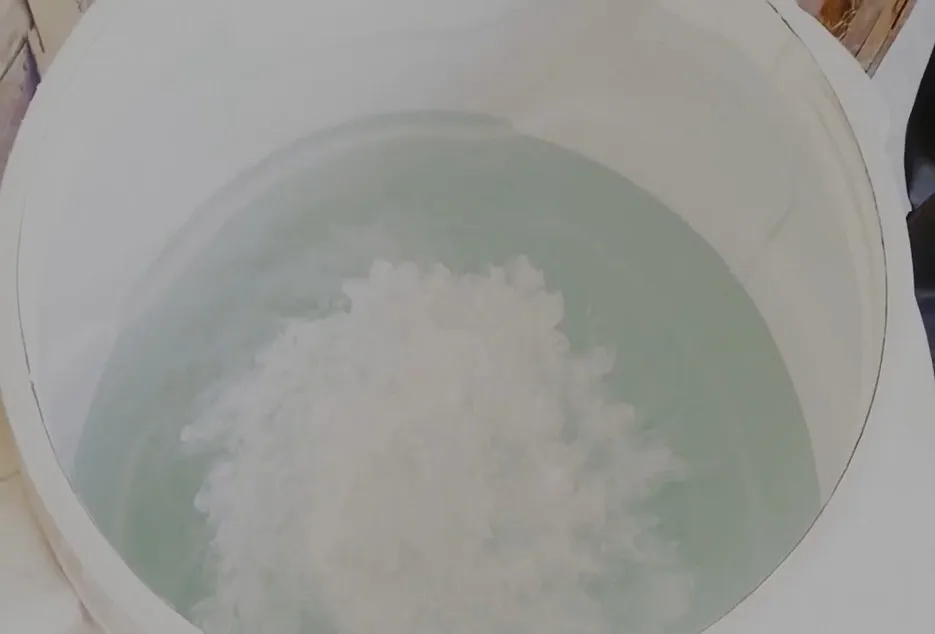
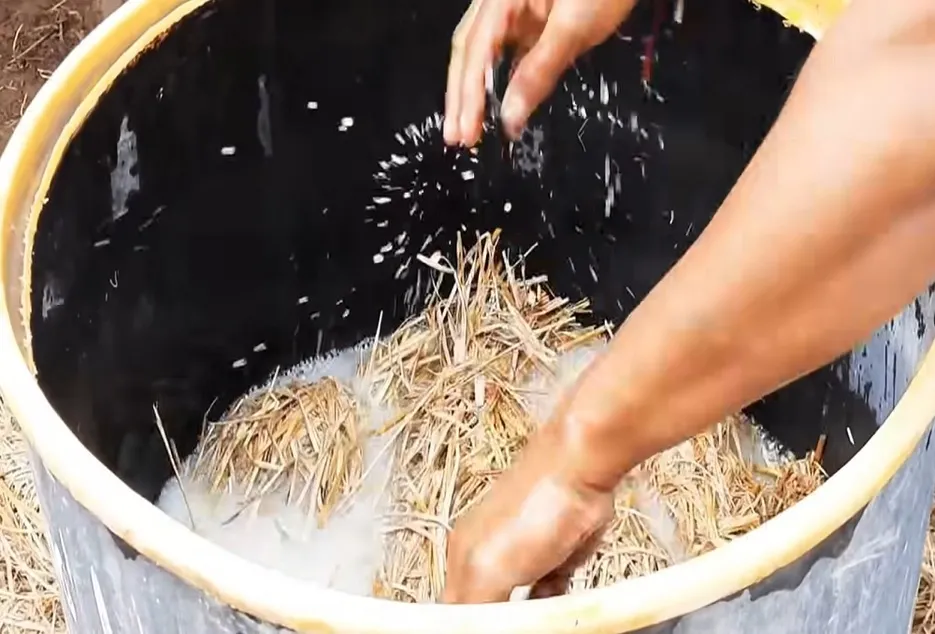
Chemical method: -
In this method, straw is treated with carbendazim and formalin. First, 90 liters of water is poured into a 200 liter drum. After this, 7.5 grams of carbendazim and 125 ml of formalin are mixed in the drum, and about 10-12 kg of dry straw is also put in the drum. After this, cover the drum with plastic foil for 14-16 hours. After the passage of 14-16 hours, the straw should be left on a plastic or iron mesh for 2-4 hours, so that the excess water comes out. This straw can then be used for mushroom cultivation.


Sowing
Sowing
Before sowing, the room where mushroom bag is to be kept should be treated with 2% formalin. For 50 kg dry straw, 5 kg seed is required. Keep in mind that the seed should not be more than 20 days old. It is necessary to select the species of mushroom according to winter and summer. For sowing, fill 4 kg of wet straw in a polythene bag with a capacity of 4 kg, about 100 grams of seeds mixed well. Take care that air does not enter the bag. Now fold the polythene and close it with a rubber band. After this, about 5 mm around the polythene. Make 10-15 holes.
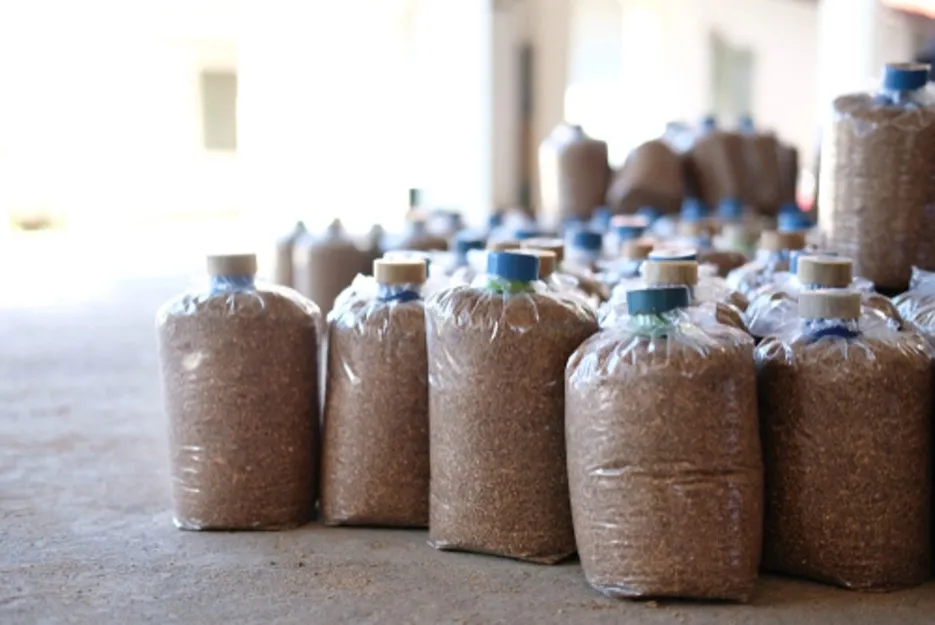


Post Sowing
Post Sowing
After seeding, the bags should be kept in the treated room, and after 2 to 4 days, the bags should be inspected, if green, black or blue mold or mold is seen in any bag, then remove such bags from the room. Should be destroyed, if the temperature of the bag and the room starts rising more than 30 ° C, then sprinkle water on the walls and ceiling of the room two to three times or use a cooler. Care should be taken that water does not accumulate on the bags. In about 15 to 25 days, the fungal web of mushroom will spread all over the straw and the bags will start appearing white. In this case the polythene should be removed. During summer (April-June) the polythene should not be completely removed as there may be loss of moisture in the bags. After removing the polythene, water should be sprayed in the room for fruiting and on the bags two to three times a day. There should be light in the room for about 6 to 8 hours or there should be tube light management in the rooms.
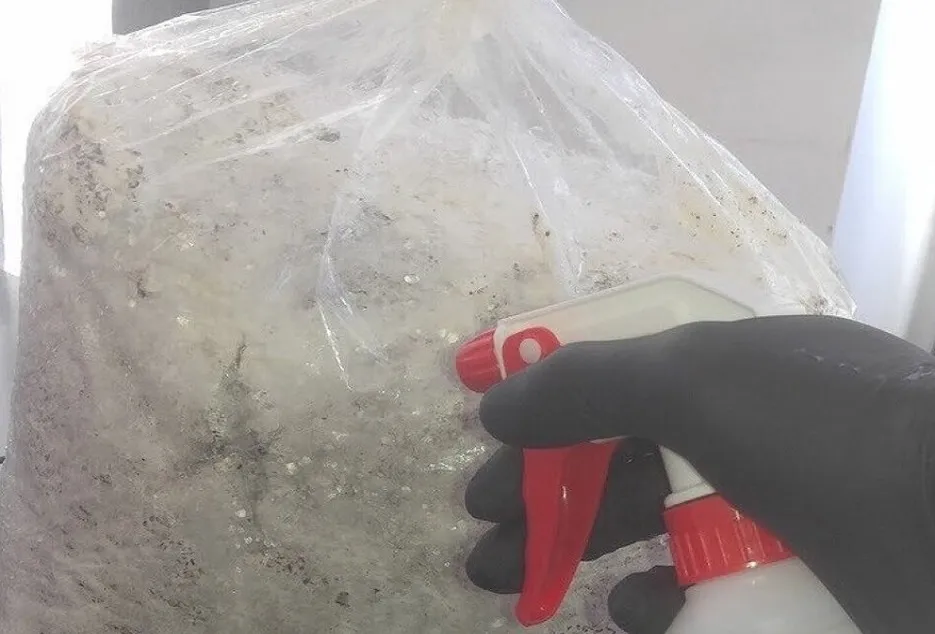


Harvest
Harvest
After about 15 to 25 days or if the outer edge of the mushroom starts turning up, then the mushroom should be harvested first. Mushroom is broken by turning the mushroom slightly from the bottom. Second harvesting can be done 8-10 days after the first crop. In this way the output can be taken three times. One kg of dry straw gives a yield of about 600 to 650 grams.
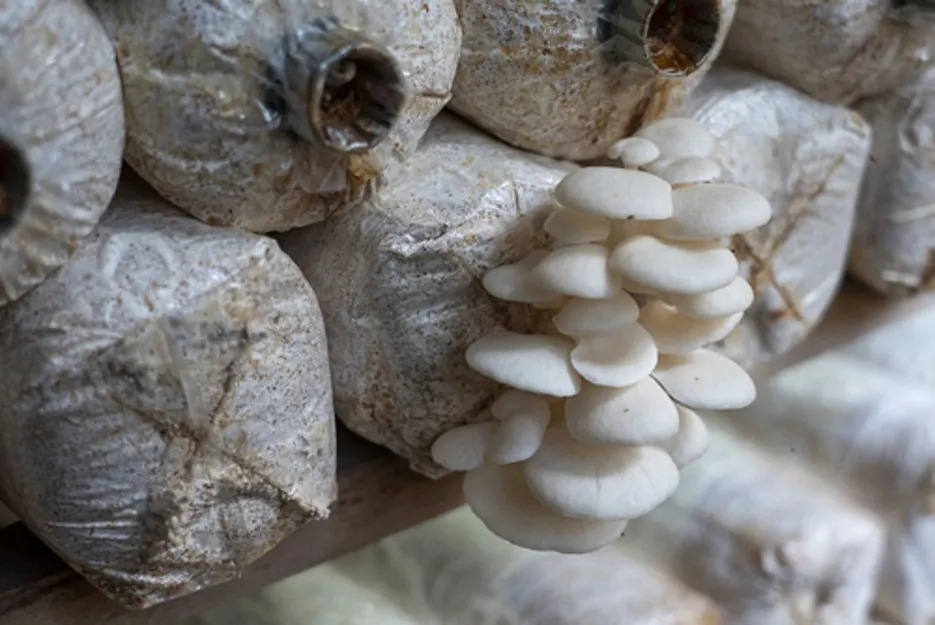
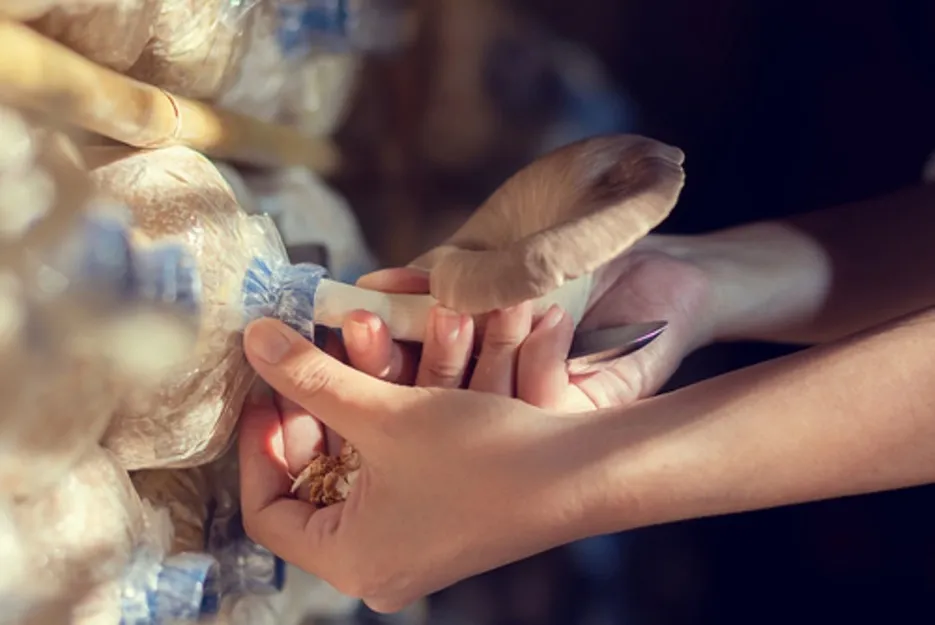


Storage / Market
Storage / Market
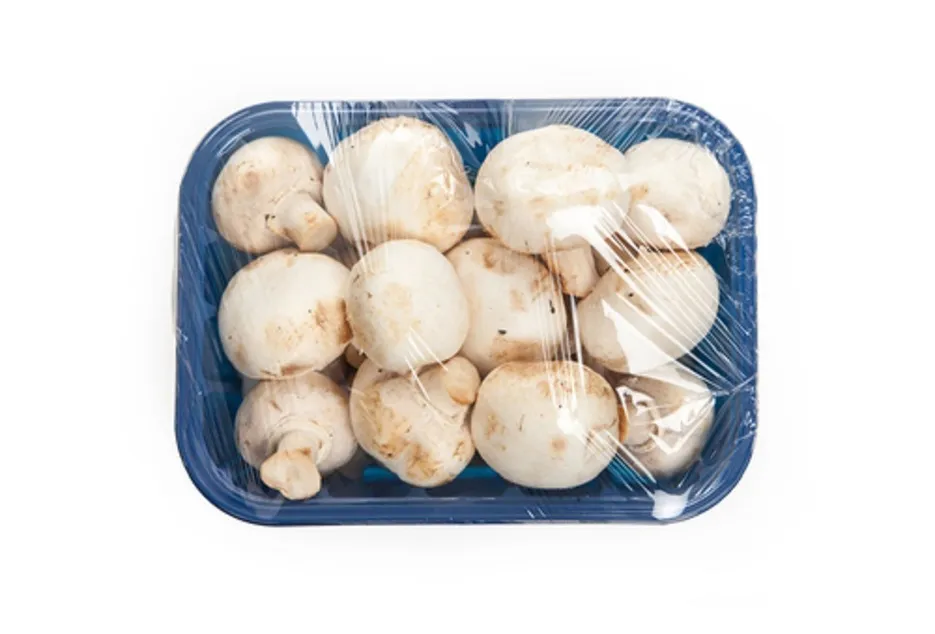
Mushrooms should not be stored in bags immediately after harvesting, they should be packed after about 3 hours, these mushrooms can be sold completely dry, the cost of cultivation of this mushroom is 10 15 per bag and the price of mushroom is 200 to 300 rupees per kg.


Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!