 Back
Back

India leads the world in banana production by accounting for 26.08% of total world banana production, which is the highest among fruit crops. Banana accounts for 13% of the total cultivable area and 1/3 rd% of the production among fruit fruits in India. The selection of planting material is very important in Banana cultivation.
How to select good planting material
How to select good planting material

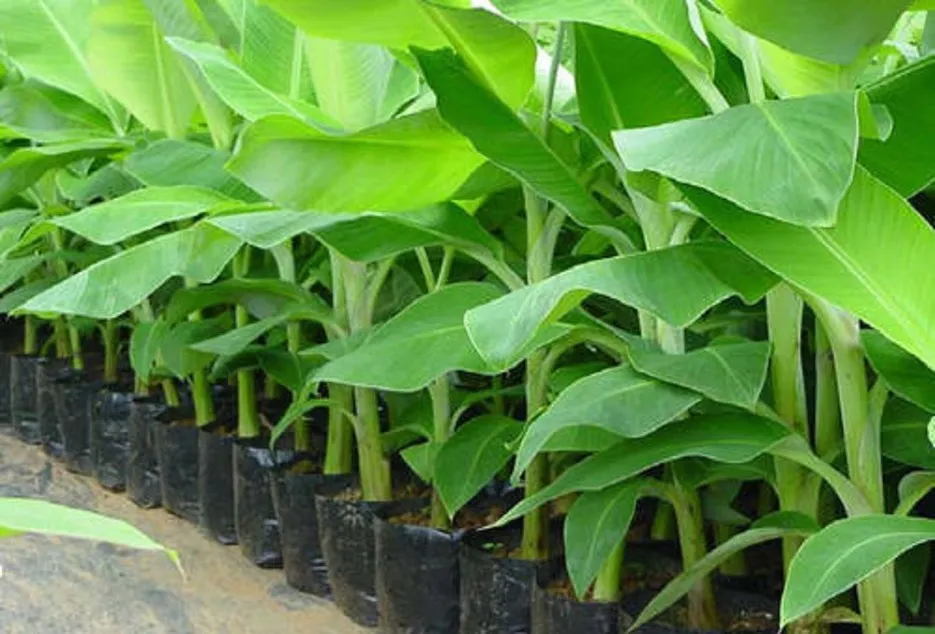
• Select 3-5 months old suckers having a uniform size.
• The weight of the suckers should be 1.0- 1.5 kg for most of the varieties except for the tall varieties like karpuravalli and monthan slightly big suckers weighing 1.5-2.0 kg should be used.
• Generally, select healthy sword suckers from wilt-free areas consist of well-developed broad corm with narrow sword-like leaves.
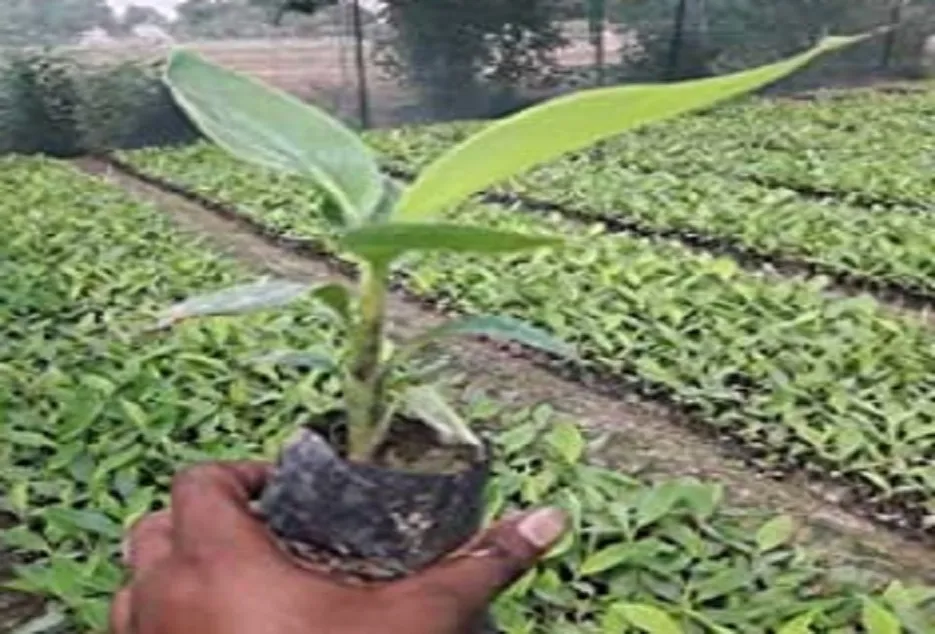




Pre-treatment of Planting material
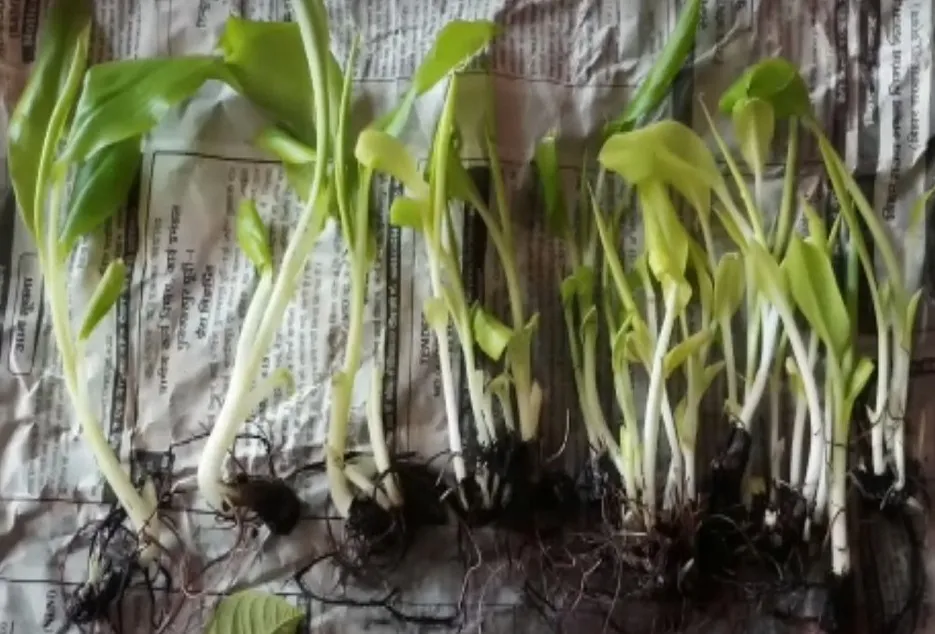
Pre-treatment of Planting material
For Tissue cultured suckers
• Tissue culture is the propagation of banana plants by using shoot tips in a test tube under controlled conditions in a soilless media. secondary hardened (45-60 days) plant of 30 cm in height, 5 cm girth is ideal for planting.
• The plant should have at least five fully opened healthy green leaves.
• Should have 25-30 active roots which are 15-20 cm in length along with a good number of secondary roots.
• Generally tissue culture plants are free from diseases, pests, and abnormal growth.


Pre planting treatment of tissue cultured plant
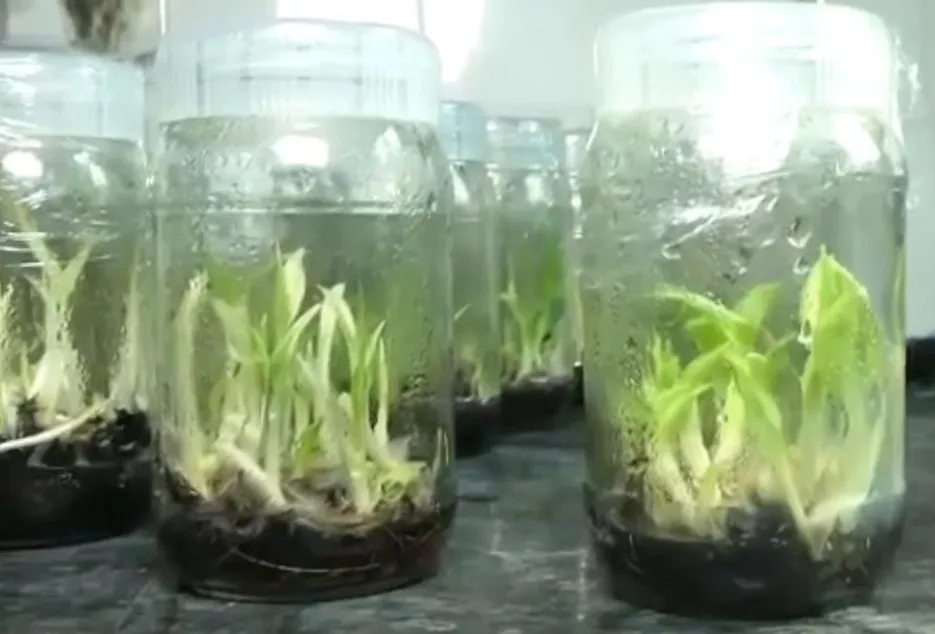
Pre planting treatment of tissue cultured plant
• One week before planting apply 10 g Carbofuron and 0.2 % Emissan in 100 ml water as drench into the polythene bags to protect against nematode infestation and bacterial rot disease respectively. For Normal suckers
• Paring: the selected suckers should be trimmed off all the roots along with surface layers superficially to remove any decayed portion of the corm. In the case of the Nendran variety, cut back pseudostem to a length of 15-20 cm from corm and remove old roots.
• Prolinge : The rhizomes are to be smeared with cow dung solution and ash and dried in the sun for about 3-4 days and stored in shade up to 15 days before planting.
• In fusarium susceptible varieties like rasthali, month,an etc, dip the pared suckers in 0.1% Carbendazim (1ml/liter of water) solution for about 25–30 minutes as a prophylactic measure against Fusarium wilt disease.
• Pared corm should be dipped in clay slurry and 40 g of Carbofuron granules per suckers to protect the plants against nematode attack.
Planting methods
Planting methods
Generally, pit methods are followed for banana cultivation in many parts of Karnataka. Suckers /plants are planted upright in small pits in the center leaving a 5 cm pseudostem above the soil. Application of 25 g Pseudomonas fluorescence per plant at the time of planting is beneficial.
- Pit method:
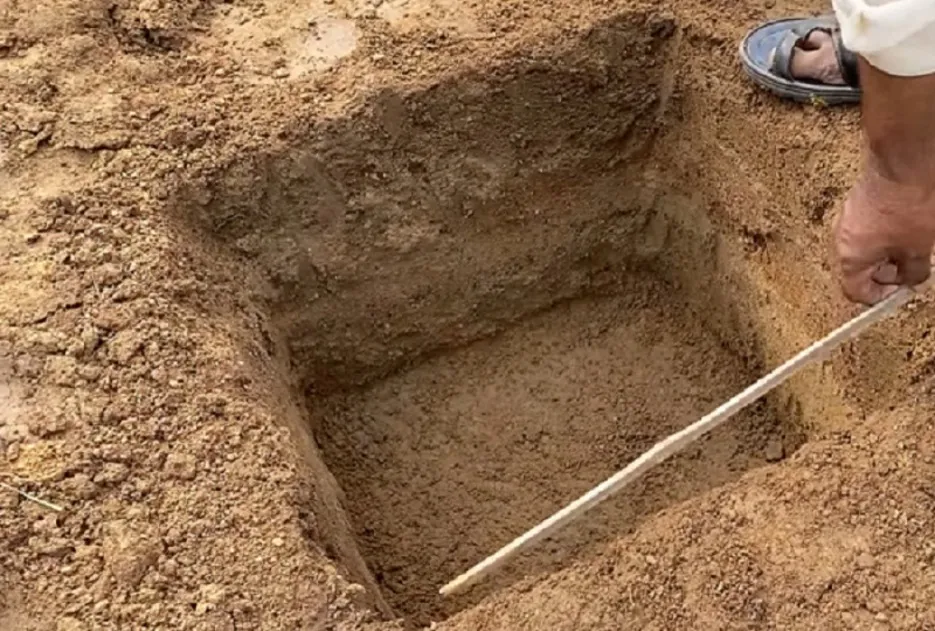
• The pits of 45 cm 3 are dug at desired spacing according to cultivars to be planted by adopting a square system
• Pits are filled with a 1:1:1 ratio of soil, sand, and FYM at least 15-30 days before planting.
• No earthing up is required since planting is done at the required depth.
• This method is laborious and expensive.


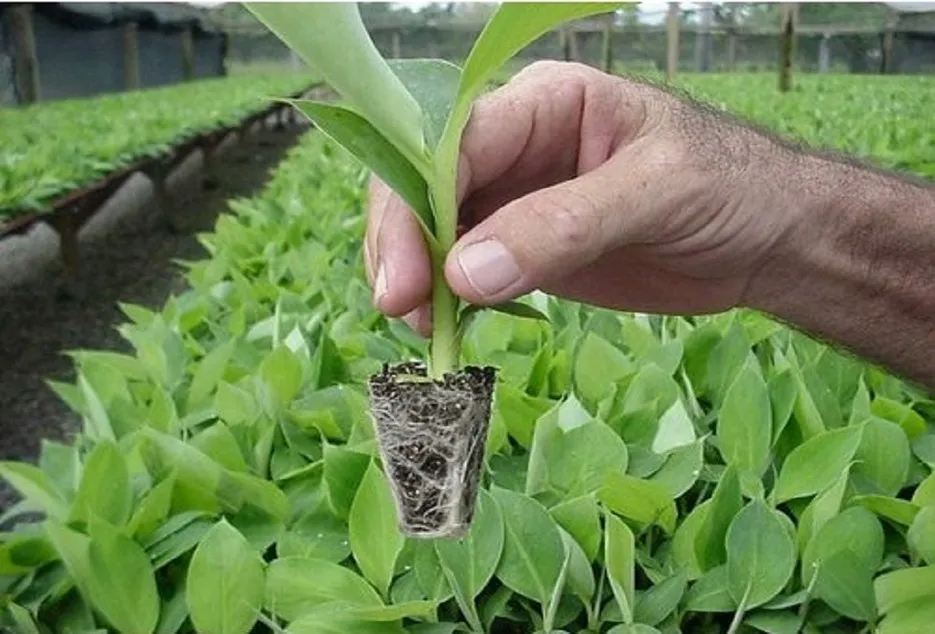
Tissue culture plants
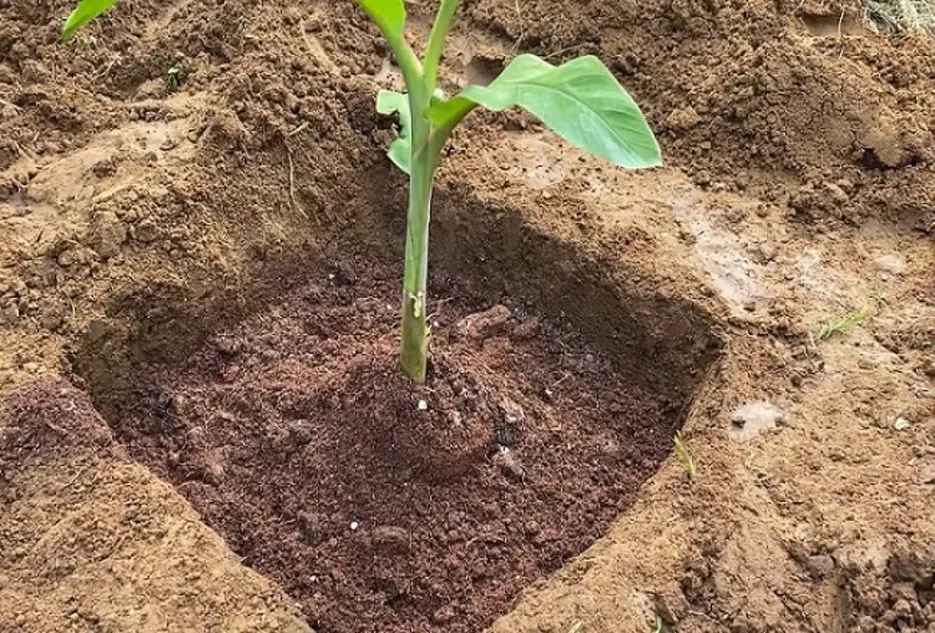
Tissue culture plants
• A pit of 30cm 3 is opened by dipping the surface soil at the desired spacing.
• The plants which have 30 cm height, 5 cm girth, and five leaves are separated from the container without disturbing the root ball and then place in pits by keeping the pseudo-stem 2cm below the ground level.
• Soils around the plant are gently pressed and avoid deep planting.


Square system
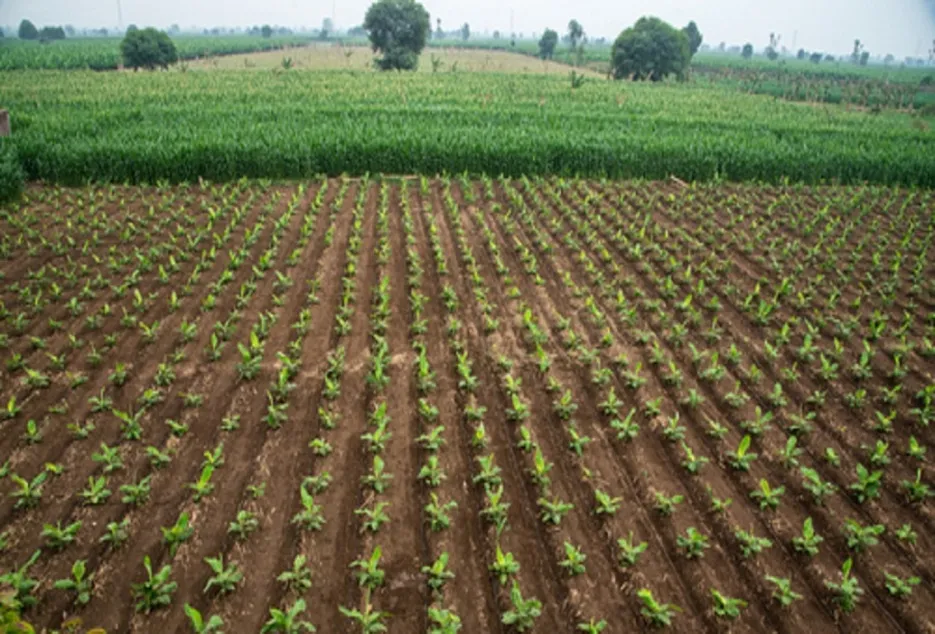
Square system
• Commonly adopted a system in India since it’s easy to layout.
• Here, suckers are planted at a corner of each square by adopting suitable spacing for cultivars.
• The central space between four plants can be used to raise filler plants and allows to take up intercropping.


Triangular system
Triangular system


• Best suited for tissue culture banana
• Similar to the square system but the difference is that plants in alternate rows are planted in the middle of two corners of the square
• This system occupies more plants than a square system.


Single row system
Single row system
• Here, suckers are planted by maintaining less distance within the row (between the plants) and maximum distance between the row.
• Merits: allows good aeration to canopy, reduces the incidence of the diseases.
• Demerits: less number of plants are occupied in the field.
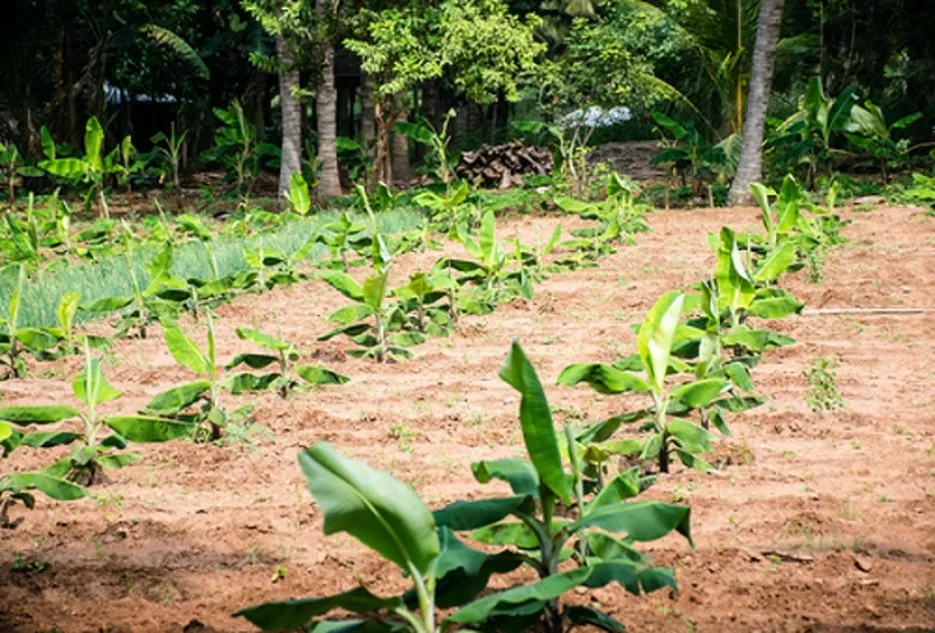


Paired row system
Paired row system
• In this system, parallel lines are opened at a distance of 1.20 -1.50 m, and suckers are planted at these parallel lines by maintaining a plant distance is 1.2-2m, and 2m spacing is left between two consecutive parallel lines to carry out intercultural operations.
Thank you for reading this article, we hope you clicked on the ♡ icon to like the article and also do share it with your friends and family now!